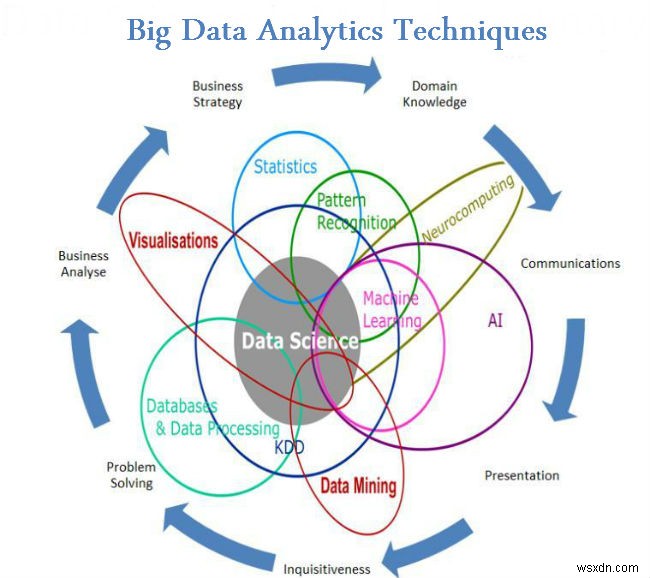
Cho đến bây giờ trong các blog của tôi về Dữ liệu lớn, tôi đã làm quen với bạn với các khía cạnh khác nhau của Dữ liệu lớn, từ Ý nghĩa thực sự của nó đến các sự kiện và những điều nên làm và không nên làm của nó. Trong blog trước, chúng ta đã thấy một số Kỹ thuật phân tích dữ liệu lớn. Xem thêm Danh sách trong blog này.
- Nhận dạng mẫu
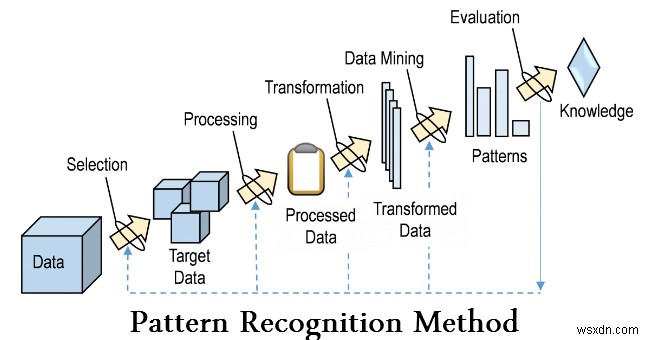
Nhận dạng mẫu là một nhánh của máy học tập trung vào việc nhận dạng các mẫu và quy luật trong dữ liệu, mặc dù trong một số trường hợp, nó được coi là gần như đồng nghĩa với học máy. Trong nhiều trường hợp, các hệ thống nhận dạng mẫu được đào tạo từ dữ liệu "đào tạo" được gắn nhãn (học có giám sát), nhưng khi không có sẵn dữ liệu được gắn nhãn, các thuật toán khác có thể được sử dụng để khám phá các mẫu chưa biết trước đó (học không giám sát).
- Mô hình dự đoán
Phân tích dự đoán bao gồm nhiều kỹ thuật dự đoán kết quả trong tương lai dựa trên dữ liệu lịch sử và hiện tại. Trên thực tế, phân tích dự đoán có thể được áp dụng cho hầu hết các lĩnh vực – từ dự đoán sự cố của động cơ phản lực dựa trên luồng dữ liệu từ hàng nghìn cảm biến, đến dự đoán hành động tiếp theo của khách hàng dựa trên những gì họ mua, thời điểm họ mua và thậm chí cả những gì họ mua. họ nói trên phương tiện truyền thông xã hội. Các kỹ thuật phân tích dự đoán chủ yếu dựa trên các phương pháp thống kê.
- Phân tích hồi quy
Đây là một kỹ thuật sử dụng các biến độc lập và cách chúng ảnh hưởng đến các biến phụ thuộc. Đây có thể là một kỹ thuật rất hữu ích trong việc xác định các phân tích mạng xã hội như xác suất tìm thấy tình yêu trên nền tảng internet.
- Phân tích cảm tính
Phân tích tình cảm giúp các nhà nghiên cứu xác định tình cảm của người nói hoặc người viết đối với một chủ đề. Phân tích cảm tính đang được sử dụng để trợ giúp:
- Cải thiện dịch vụ tại chuỗi khách sạn bằng cách phân tích nhận xét của khách.
- Tùy chỉnh các ưu đãi và dịch vụ để đáp ứng nhu cầu thực sự của khách hàng.
- Xác định suy nghĩ thực sự của người tiêu dùng dựa trên ý kiến từ mạng xã hội.
- Xử lý tín hiệu
Xử lý tín hiệu là một công nghệ cho phép bao gồm lý thuyết cơ bản, ứng dụng, thuật toán và triển khai xử lý hoặc truyền thông tin chứa trong nhiều định dạng vật lý, biểu tượng hoặc trừu tượng khác nhau được chỉ định rộng rãi là tín hiệu . Nó sử dụng các biểu diễn toán học, thống kê, tính toán, heuristic và ngôn ngữ, hình thức và kỹ thuật để biểu diễn, mô hình hóa, phân tích, tổng hợp, khám phá, phục hồi, cảm biến, thu thập, trích xuất, học tập, bảo mật hoặc pháp y. Các ứng dụng mẫu bao gồm lập mô hình để phân tích chuỗi thời gian hoặc triển khai hợp nhất dữ liệu để xác định giá trị đọc chính xác hơn bằng cách kết hợp dữ liệu từ một tập hợp các nguồn dữ liệu kém chính xác hơn (nghĩa là trích xuất tín hiệu từ nhiễu).
- Phân tích không gian
Phân tích không gian là quá trình chúng tôi biến dữ liệu thô thành thông tin hữu ích. It is the process of examining the locations, attributes, and relationships of features in spatial data through overlay and other analytical techniques in order to address a question or gain useful knowledge. Spatial analysis extracts or creates new information from spatial data.
- Statistics
In statistics, exploratory data analysis is an approach to analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often with visual methods. A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell us beyond the formal modelling or hypothesis testing task. Statistical techniques are also used to reduce the likelihood of Type I errors (“false positives”) and Type II errors (“false negatives”). An example of an application is A/B testing to determine what types of marketing material will most increase revenue.
- Supervised learning
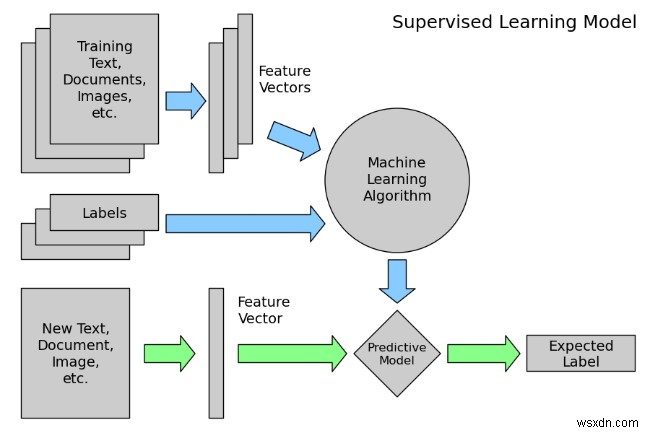
Supervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function from labeled training data. The training data consist of a set of training examples . In supervised learning, each example is a pair consisting of an input object (typically a vector) and a desired output value (also called the supervisory signal ). A supervised learning algorithm analyzes the training data and produces an inferred function, which can be used for mapping new examples.
- Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis is a technique that was first used in the telecommunications industry, and then quickly adopted by sociologists to study interpersonal relationships. It is now being applied to analyze the relationships between people in many fields and commercial activities. Nodes represent individuals within a network, while ties represent the relationships between the individuals.
- Simulation
Modeling the behavior of complex systems, often used for forecasting, predicting and scenario planning. Monte Carlo simulations, for example, are a class of algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling, i.e., running thousands of simulations, each based on different assumptions. The result is a histogram that gives a probability distribution of outcomes. One application is assessing the likelihood of meeting financial targets given uncertainties about the success of various initiatives
- Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series data often arise when monitoring industrial processes or tracking corporate business metrics. Time series analysis accounts for the fact that data points taken over time may have an internal structure (such as autocorrelation, trend or seasonal variation) that should be accounted for. Examples of time series analysis include the hourly value of a stock market index or the number of patients diagnosed with a given condition every day.
- Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is the machine learning task of inferring a function to describe hidden structure from unlabeled data. Since the examples given to the learner are unlabeled, there is no error or reward signal to evaluate a potential solution – this distinguishes unsupervised learning from supervised learning and reinforcement learning.
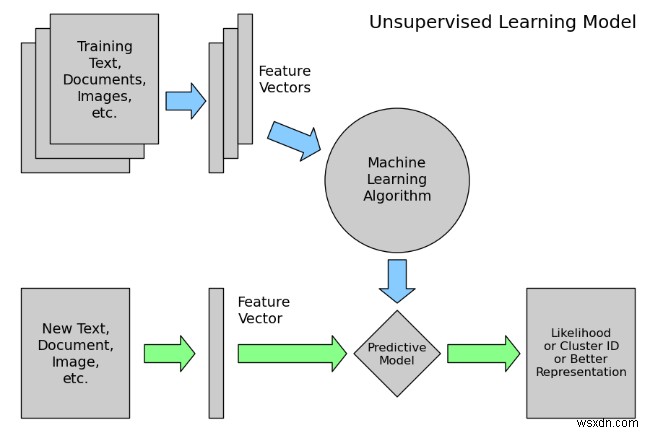
However, unsupervised learning also encompasses many other techniques that seek to summarize and explain key features of the data.
- Visualization
Data visualization is the preparation of data in a pictorial or graphical format. It enables decision makers to see analytics presented visually, so they can grasp difficult concepts or identify new patterns. With interactive visualization, you can take the concept a step further by using technology to drill down into charts and graphs for more detail, interactively changing what data you see and how it’s processed.
Conclusion
Big data analytics has been one of the most important breakthroughs in the information technology industry. In fact, Big Data has shown its importance and need almost in all sectors, and in all the departments of those industries. There is not a single aspect of life which has not been affected by Big Data, not even our personal lives. Hence we need Big Data Analytics to manage this huge amounts of Data efficiently.
As said before this list is not exhaustive. Researchers are still experimenting on new ways of Analyzing this huge amounts of Data which is present in a variety of forms whose speed of generation is increasing with time to derive values for our specific uses.
