Trong một đồ thị có hướng được cho là có liên kết chặt chẽ, khi có một đường đi giữa mỗi cặp đỉnh trong một thành phần.
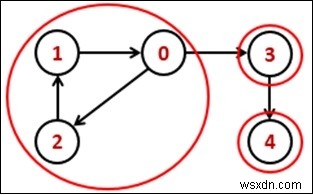
Để giải thuật toán này, trước hết, thuật toán DFS được sử dụng để lấy thời gian kết thúc của mỗi đỉnh, bây giờ tìm thời gian kết thúc của đồ thị chuyển vị, sau đó các đỉnh được sắp xếp theo thứ tự giảm dần theo cách sắp xếp tôpô.
Đầu vào và Đầu ra
Input: Adjacency matrix of the graph. 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 Output: Following are strongly connected components in given graph: 0 1 2 3 4
Thuật toán
đi ngang (biểu đồ, bắt đầu, đã truy cập)
Đầu vào: Biểu đồ sẽ được duyệt qua, đỉnh bắt đầu và cờ của các nút đã truy cập.
Đầu ra: Đi qua từng nút trong kỹ thuật DFS và các nút hiển thị.
Begin mark start as visited for all vertices v connected with start, do if v is not visited, then traverse(graph, v, visited) done End
topoSort (u, đã truy cập, ngăn xếp)
Đầu vào - Nút bắt đầu, cờ cho các đỉnh đã thăm, ngăn xếp.
Đầu ra - Điền vào ngăn xếp trong khi sắp xếp biểu đồ.
Begin mark u as visited for all node v, connected with u, do if v is not visited, then topoSort(v, visited, stack) done push u into the stack End
getStrongConComponents (đồ thị)
Đầu vào: Biểu đồ đã cho.
Đầu ra - Tất cả các thành phần được kết nối mạnh mẽ.
Begin initially all nodes are unvisited for all vertex i in the graph, do if i is not visited, then topoSort(i, vis, stack) done make all nodes unvisited again transGraph := transpose of given graph while stack is not empty, do pop node from stack and take into v if v is not visited, then traverse(transGraph, v, visited) done End
Ví dụ
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int transGraph[NODE][NODE];
void transpose() { //transpose the graph and store to transGraph
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++)
transGraph[i][j] = graph[j][i];
}
void traverse(int g[NODE][NODE], int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
cout << u << " ";
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(g[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(g, v, visited);
}
}
}
void topoSort(int u, bool visited[], stack<int>&stk) {
visited[u] = true; //set as the node v is visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) { //for allvertices v adjacent to u
if(!visited[v])
topoSort(v, visited, stk);
}
}
stk.push(u); //push starting vertex into the stack
}
void getStrongConComponents() {
stack<int> stk;
bool vis[NODE];
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initially all nodes are unvisited
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
if(!vis[i]) //when node is not visited
topoSort(i, vis, stk);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //make all nodes are unvisited for traversal
transpose(); //make reversed graph
while(!stk.empty()) { //when stack contains element, process in topological order
int v = stk.top(); stk.pop();
if(!vis[v]) {
traverse(transGraph, v, vis);
cout << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
cout << "Following are strongly connected components in given graph: "<<endl;
getStrongConComponents();
} Đầu ra
Following are strongly connected components in given graph: 0 1 2 3 4
