Thuật toán Ford-Fulkerson được sử dụng để phát hiện luồng cực đại từ đỉnh bắt đầu đến đỉnh chìm trong một đồ thị nhất định. Trong đồ thị này, mọi cạnh đều có công suất. Hai đỉnh được cung cấp có tên Nguồn và Chìm. Đỉnh nguồn có tất cả cạnh ra ngoài, không có cạnh trong và phần chìm sẽ có tất cả cạnh vào trong không có cạnh ra ngoài.
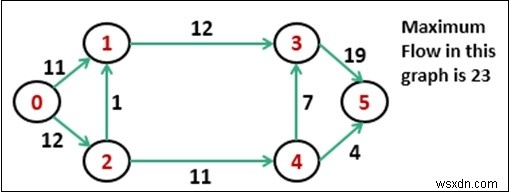
Có một số ràng buộc:
- Dòng chảy trên một cạnh không vượt quá khả năng nhất định của biểu đồ đó.
- Luồng đến và luồng đi cũng sẽ bằng nhau đối với mọi cạnh, ngoại trừ nguồn và bồn rửa.
Đầu vào và Đầu ra
Input: The adjacency matrix: 0 10 0 10 0 0 0 0 4 2 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 0 6 0 0 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 Output: Maximum flow is: 19
Thuật toán
bfs (vert, bắt đầu, chìm)
Đầu vào: Danh sách đỉnh, nút bắt đầu và nút chìm.
Đầu ra - Đúng khi bồn rửa được truy cập.
Begin initially mark all nodes as unvisited state of start as visited predecessor of start node is φ insert start into the queue qu while qu is not empty, do delete element from queue and set to vertex u for all vertices i, in the residual graph, do if u and i are connected, and i is unvisited, then add vertex i into the queue predecessor of i is u mark i as visited done done return true if state of sink vertex is visited End
fordFulkerson (vert, nguồn, chìm)
Đầu vào: Danh sách đỉnh, đỉnh nguồn và đỉnh chìm.
Đầu ra - Lưu lượng tối đa từ đầu đến chìm.
Begin create a residual graph and copy given graph into it while bfs(vert, source, sink) is true, do pathFlow := ∞ v := sink vertex while v ≠ start vertex, do u := predecessor of v pathFlow := minimum of pathFlow and residualGraph[u, v] v := predecessor of v done v := sink vertex while v ≠ start vertex, do u := predecessor of v residualGraph[u,v] := residualGraph[u,v] – pathFlow residualGraph[v,u] := residualGraph[v,u] – pathFlow v := predecessor of v done maFlow := maxFlow + pathFlow done return maxFlow End
Ví dụ
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#define NODE 6
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int val;
int state; //status
int pred; //predecessor
}node;
int minimum(int a, int b) {
return (a<b)?a:b;
}
int resGraph[NODE][NODE];
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
{0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
}; */
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 10, 0, 10, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 4, 2, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 10},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0},
{0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 10},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int bfs(node *vert, node start, node sink) {
node u;
int i, j;
queue<node> que;
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vert[i].state = 0; //not visited
}
vert[start.val].state = 1; //visited
vert[start.val].pred = -1; //no parent node
que.push(start); //insert starting node
while(!que.empty()) {
//delete from queue and print
u = que.front();
que.pop();
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(resGraph[u.val][i] > 0 && vert[i].state == 0) {
que.push(vert[i]);
vert[i].pred = u.val;
vert[i].state = 1;
}
}
}
return (vert[sink.val].state == 1);
}
int fordFulkerson(node *vert, node source, node sink) {
int maxFlow = 0;
int u, v;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
resGraph[i][j] = graph[i][j]; //initially residual graph is main graph
}
}
while(bfs(vert, source, sink)) { //find augmented path using bfs algorithm
int pathFlow = 999;//as infinity
for(v = sink.val; v != source.val; v=vert[v].pred) {
u = vert[v].pred;
pathFlow = minimum(pathFlow, resGraph[u][v]);
}
for(v = sink.val; v != source.val; v=vert[v].pred) {
u = vert[v].pred;
resGraph[u][v] -= pathFlow; //update residual capacity of edges
resGraph[v][u] += pathFlow; //update residual capacity of reverse edges
}
maxFlow += pathFlow;
}
return maxFlow; //the overall max flow
}
int main() {
node vertices[NODE];
node source, sink;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vertices[i].val = i;
}
source.val = 0;
sink.val = 5;
int maxFlow = fordFulkerson(vertices, source, sink);
cout << "Maximum flow is: " << maxFlow << endl;
} Đầu ra
Maximum flow is: 19
