Trong hệ điều hành Linux, một tệp đã xóa sẽ tìm đường vào Thùng rác. Khi Thùng rác được dọn sạch, tệp sẽ bị xóa khỏi hệ thống. Tuy nhiên, với nhu cầu ngày càng tăng về phần mềm khôi phục, các tệp bị xóa khỏi Thùng rác có thể được khôi phục ở một mức độ nhất định. Điều này có nghĩa là tệp đã bị xóa khỏi Thùng rác không bao giờ bị xóa vĩnh viễn mà chỉ trở nên vô hình trước mắt bạn. Tệp vẫn ở đâu đó trên ổ cứng chiếm dung lượng không cần thiết và sẽ chỉ bị xóa hoàn toàn khi một tệp mới được tạo và được lưu trữ trên cùng các khu vực đó của ổ cứng. Để khôi phục dung lượng đĩa quý giá và tránh hỏng tệp, điều quan trọng là phải xóa vĩnh viễn một tệp trong Linux.
Dưới đây là một số bước để xóa vĩnh viễn tệp trong hệ điều hành Linux.
Do các biến thể có trong hệ điều hành Linux và một số Distro có sẵn như Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora, v.v., các bước để xóa tệp trong Linux có thể khác nhau về các bước, nhưng khái niệm cơ bản đằng sau việc xóa tệp và thư mục vẫn giống nhau. Các bước phổ biến nhất có thể xóa vĩnh viễn các thư mục trong Linux mà không cần phải định dạng Đĩa cứng của bạn là:
Phương pháp 1. Xóa Tùy chọn Thùng rác
Có một tùy chọn, khi được chọn, cho phép người dùng xóa trực tiếp một tệp trong Linux mà không gửi chúng vào thùng rác. Việc bật tùy chọn này khác nhau ở các loại Linux khác nhau, nhưng quy trình được sử dụng đằng sau tính năng này có thể là một trong hai quy trình được đề cập bên dưới:
- Giảm giới hạn thùng rác.
Nếu bản phân phối Linux của bạn hỗ trợ trình quản lý tệp Dolphin, hãy truy cập tùy chọn và đánh dấu kiểm bên cạnh hộp có nhãn Kích thước và đặt giới hạn phần trăm thành giá trị thấp nhất. Điều này sẽ đảm bảo rằng tất cả các tệp lớn hơn kích thước đã đặt sẽ không được lưu trữ trong Thùng rác và sẽ bị xóa vĩnh viễn.
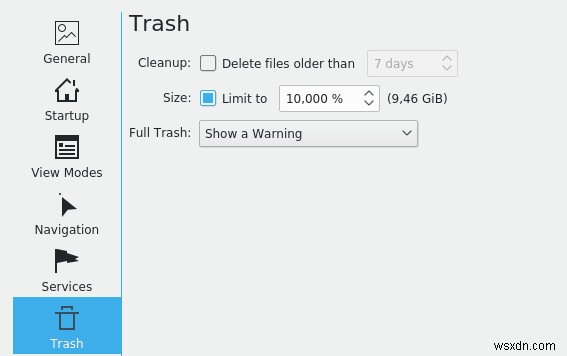
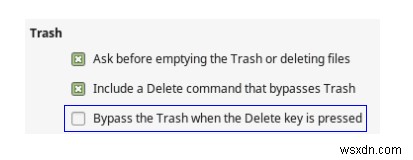
- Nếu Linux của bạn đang sử dụng trình quản lý tệp Nautilus hoặc Nemo thì bạn sẽ có một tùy chọn trong Tùy chọn trình quản lý tệp để bật Bỏ qua thùng rác khi nhấn phím Delete. Thao tác này sẽ không chuyển bất kỳ tệp đã xóa nào vào Thùng rác.
Phương pháp 2. Bạn luôn có thể Cắt nhỏ tệp
Được phát triển bởi GNU Project, Shred là một chương trình được nhúng trong hệ điều hành Linux, có thể được sử dụng để xóa vĩnh viễn một tệp trong Linux. Dòng lệnh xóa tệp tài liệu có tên Kiểm tra bằng Shred là:
shred -uvz -n 2 Test.doc
Tham số “u” xóa tệp trước khi ghi đè lên.
Tham số “v” hiển thị thông tin chi tiết.
Tham số “z” ngăn mọi cơ hội khôi phục dữ liệu đã xóa.
Tham số “-n 2” chỉ định các lượt truy cập bổ sung để tăng cường bảo mật.
In case, there are multiple files in a folder by the name of Music and you want to delete all of them, then use this command:
shred -uvz -n 2 Music/*.*
The name of the folder is specified as Music and the Asterix with a period and followed by another Asterix specifies to delete a file in Linux irrespective of their name or extension.
Method 3. Use Wipe.
The Linux Software distribution centre will allow you to install Wipe on your Linux Distro. It is like Shred program and is easy to use. The command line for deleting a file through Wipe is:
wipe Music/song1.mp3
Wipe is more secure than Shred and this means it is time-consuming as well. It also requests a confirmation from the user. To quicken the process, use appropriate flags such as:
f:using this flag will remove the confirmation.
c:wipe the file despite permissions.
q:quicken the process by bypassing all the security passes.
r:delete from a folder in Linux.
The simple Wipe command with all the flags would now appear as:
wipe -rfcq Music/song1.mp3
Method 4. Use Secure Delete.
Another tool that ensures removal of data from a hard drive is SRM, which is bundled in the Secure Delete suite. It is a quite efficient and quick tool and can even delete a directory in Linux. The command to delete a file is:
SRM is one of the tools in the Secure Delete suite of tools that specializes in secure removal of data from your HDD. It’s held by many as the best tool for this job.
Srm Music/song1.mp3
Like Wipe, deleting a file by SRM is a time-consuming process and can be made aster using flags. Some important flags are:
z:your file will be deleted and overwritten by zeros replacing the file for extra security.
v:this flag will provide verbose information about the process.
r:this will enable the recursive mode for subfolders.
1:the number one. This will reduce the time taken to complete the process.
The new command would then be:
srm -rlvz Music/Song1.jpg
Method 5. Install Bleachbit (GUI)
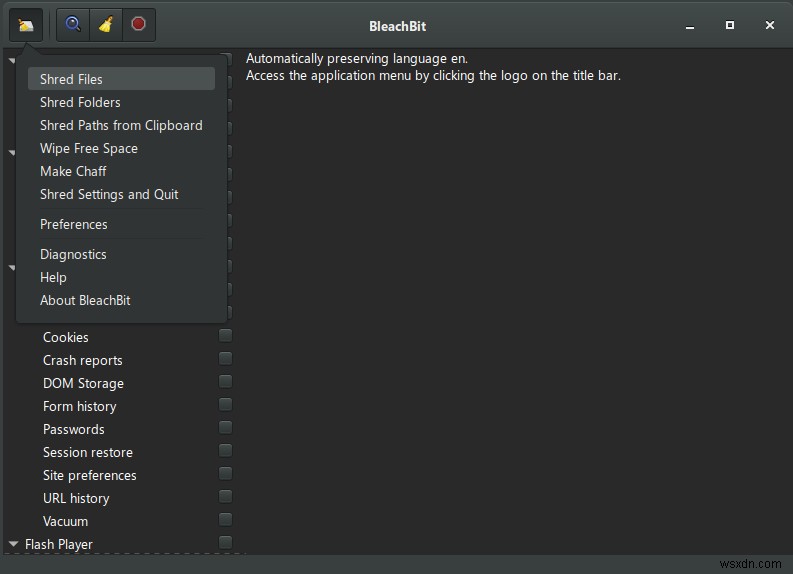
One of the best tools to find and delete unwanted files and even delete folders in Linux operating system is Bleachbit. It is known to free up space by securely erasing data that has not been used for a long time and can be used manually to target a few files that need to be deleted. It can be installed through the software centre by using the following command:
sudo apt install bleachbit
Once installed, run the interface and click on EDIT and choose Preferences. In the General Tab, there would be a list of different options. Place a checkmark in the box beside the option labelled as “Overwrite contents of files to prevent recovery”.
Next, to permanently delete a file on Linux, click File and choose Shred option. A prompt box will appear confirming your action. Click on Delete, and that will the last of the files selected.
The Final Word On Delete A File In Linux.
Although using a Linux operating system is a different experience, it is not difficult. All you must know the functions and features that are embedded in Linux. Being an Open-source, Linux has many options to do the same task, and these are some of the easy ones to delete a file in Linux permanently. Do subscribe to Systweak Blogs and our YouTube Channel for more tech-related updates.
