Thuật toán đường đi ngắn nhất nguồn đơn (đối với trọng số dương hoặc âm tùy ý) còn được gọi là thuật toán Bellman-Ford được sử dụng để tìm khoảng cách tối thiểu từ đỉnh nguồn đến bất kỳ đỉnh nào khác. Sự khác biệt chính giữa thuật toán này với thuật toán Dijkstra là, trong thuật toán Dijkstra, chúng tôi không thể xử lý trọng số âm, nhưng ở đây chúng tôi có thể xử lý nó một cách dễ dàng.
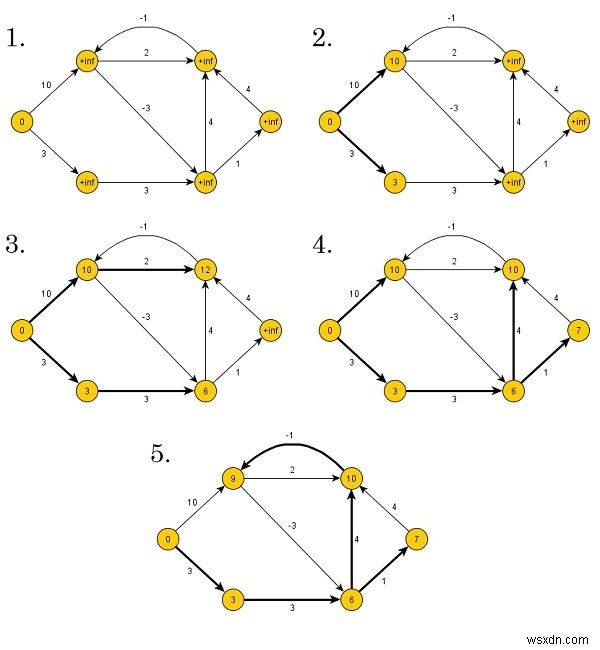
Thuật toán Bellman-Ford tìm khoảng cách theo cách từ dưới lên. Lúc đầu, nó tìm những khoảng cách chỉ có một cạnh trên đường đi. Sau đó, hãy tăng độ dài đường dẫn để tìm tất cả các giải pháp khả thi.
Đầu vào - Ma trận chi phí của biểu đồ:
0 6 ∞ 7 ∞ ∞ 0 5 8 -4 ∞ -2 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ -3 0 9 2 ∞ 7 ∞ 0
Đầu ra - Nguồn Vertex:2
Vert:0 1 2 3 4
Quận:-4 -2 0 3 -6
Dự đoán:4 2 -1 0 1
Biểu đồ không có chu trình cạnh âm
Thuật toán
bellmanFord (dist, trước, nguồn)
Đầu vào - Danh sách khoảng cách, danh sách tiền nhiệm và đỉnh nguồn.
Đầu ra - Đúng, khi một chu kỳ âm được tìm thấy.
Begin iCount := 1 maxEdge := n * (n - 1) / 2 //n is number of vertices for all vertices v of the graph, do dist[v] := ∞ pred[v] := ϕ done dist[source] := 0 eCount := number of edges present in the graph create edge list named edgeList while iCount < n, do for i := 0 to eCount, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) pred[edgeList[i].v] := edgeList[i].u done done iCount := iCount + 1 for all vertices i in the graph, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i), then return true done return false End
Ví dụ (C ++)
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define V 5
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph (directed) vertex 5
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 6, INF, 7, INF},
{INF, 0, 5, 8, -4},
{INF, -2, 0, INF, INF},
{INF, INF, -3, 0, 9},
{2, INF, 7, INF, 0}
};
typedef struct{
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
int isDiagraph(){
//check the graph is directed graph or not
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(j = 0; j<V; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != costMat[j][i]){
return 1;//graph is directed
}
}
}
return 0;//graph is undirected
}
int makeEdgeList(edge *eList){
//create edgelist from the edges of graph
int count = -1;
if(isDiagraph()){
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<V; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != 0 && costMat[i][j] != INF){
count++;//edge find when graph is directed
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}else{
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<i; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != INF){
count++;//edge find when graph is undirected
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return count+1;
}
int bellmanFord(int *dist, int *pred,int src){
int icount = 1, ecount, max = V*(V-1)/2;
edge edgeList[max];
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
dist[i] = INF;//initialize with infinity
pred[i] = -1;//no predecessor found.
}
dist[src] = 0;//for starting vertex, distance is 0
ecount = makeEdgeList(edgeList); //edgeList formation
while(icount < V){ //number of iteration is (Vertex - 1)
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++){
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]){
//relax edge and set predecessor
dist[edgeList[i].v] = dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v];
pred[edgeList[i].v] = edgeList[i].u;
}
}
icount++;
}
//test for negative cycle
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++){
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]){
return 1;//indicates the graph has negative cycle
}
}
return 0;//no negative cycle
}
void display(int *dist, int *pred){
cout << "Vert: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout <<setw(3) << i << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Dist: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << dist[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Pred: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << pred[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
int dist[V], pred[V], source, report;
source = 2;
report = bellmanFord(dist, pred, source);
cout << "Source Vertex: " << source<<endl;
display(dist, pred);
if(report)
cout << "The graph has a negative edge cycle" << endl;
else
cout << "The graph has no negative edge cycle" << endl;
} Đầu ra
Source Vertex: 2 Vert: 0 1 2 3 4 Dist: -4 -2 0 3 -6 Pred: 4 2 -1 0 1 The graph has no negative edge cycle
