Cho một ma trận M [r] [c], ‘r’ biểu thị số hàng và ‘c’ biểu thị số cột sao cho r =c tạo thành một ma trận vuông. Chúng ta phải tìm xem ma trận vuông đã cho có phải là đường chéo hay không và vô hướng ma trận hoặc không, nếu nó là đường chéo và vô hướng sau đó in có trong kết quả.
Ma trận đường chéo
Ma trận vuông m [] [] sẽ là ma trận đường chéo nếu và chỉ khi các phần tử của ngoại trừ đường chéo chính bằng không.
Như trong hình bên dưới -
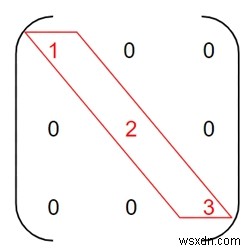
Ở đây, các phần tử có màu đỏ là đường chéo chính là các phần tử còn lại khác 0 ngoại trừ đường chéo chính bằng 0 làm cho nó trở thành Ma trận đường chéo .
Ví dụ
Input: m[3][3] = { {7, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 9}}
Output: yes
Input: m[3][3] = { {1, 2, 3},
{0, 4, 0},
{0, 0, 5}
}
Output: no Thuật toán
Start
Step 1 -> define macro of size 4
Step 2 -> declare function to check if matrix is diagonal or not
bool ifdiagonal(int arr[size][size])
Loop For int i = 0 and i < size and i++
Loop for int j = 0 and j < size and j++
IF ((i != j) & (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false
End
End
End
return true
step 3 -> In main()
Declare and set int arr[size][size] = { { 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1 }
};
IF (ifdiagonal(arr))
Print its a diagonal matrix
End
Else
Print its not a diagonal matrix
End
Stop Ma trận đường chéo
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define size 4
using namespace std;
// check if matrix is diagonal matrix or not.
bool ifdiagonal(int arr[size][size]){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
if ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
int arr[size][size] = { { 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1 }
};
if (ifdiagonal(arr))
cout << "its a diagonal matrix" << endl;
else
cout << "its not a diagonal matrix" << endl;
return 0;
} Đầu ra
its a diagonal matrix
BIỂU DIỄN MÀN HÌNH
Ma trận vuông m [] [] là Ma trận vô hướng nếu các phần tử trong đường chéo chính bằng nhau và các phần tử còn lại bằng không.
Giống như trong ví dụ cho sẵn bên dưới -
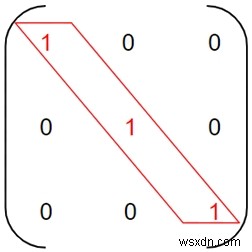
Ở đây, các phần tử có màu đỏ là các phần tử đường chéo giống nhau và các phần tử còn lại bằng 0 làm cho nó trở thành Ma trận vô hướng .
Ví dụ
Input: m[3][3] = { {2, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 0},
{0, 0, 2} }
Output: yes
Input: m[3][3] = { {3, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 0},
{0, 0, 3} }
Output: no Thuật toán
Start
Step 1 -> Declare macro as #define size 4
Step 2 -> declare function to check matrix is scalar matrix or not.
bool scalar(int arr[size][size])
Loop For int i = 0 and i < size and i++
Loop For int j = 0 and j < size and j++
IF ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false
End
End
End
Loop for int i = 0 and i < size – 1 and i++
If (arr[i][i] != arr[i + 1][i + 1])
return false
End
End
Return true
Step 3 -> In main()
Declare array as int arr[size][size] = { { 2, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2 }
}
IF(scalar(arr))
Print its a scalar matrix
Else
Print its not a scalar matrix
Stop Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define size 4
using namespace std;
// check matrix is scalar matrix or not.
bool scalar(int arr[size][size]){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
if ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
if (arr[i][i] != arr[i + 1][i + 1])
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
int arr[size][size] = { { 2, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2 } };
if (scalar(arr))
cout << "its a scalar matrix" << endl;
else
cout << "its not a scalar matrix" << endl;
return 0;
} Đầu ra
its a scalar matrix
