Cấu trúc dữ liệu là tập hợp dữ liệu được tổ chức theo một cách có cấu trúc. Nó được chia thành hai loại như được giải thích bên dưới -
-
Cấu trúc dữ liệu tuyến tính - Dữ liệu được tổ chức theo kiểu tuyến tính. Ví dụ:mảng, cấu trúc, ngăn xếp, hàng đợi, danh sách được liên kết.
-
Cấu trúc dữ liệu phi tuyến - Dữ liệu được tổ chức một cách phân cấp. Ví dụ:Cây, đồ thị, tập hợp, bảng.
Hàng đợi
Đây là một cấu trúc dữ liệu tuyến tính, trong đó việc chèn được thực hiện ở phía sau và việc xóa được thực hiện ở phía trước.
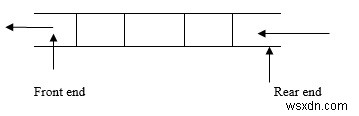
Thứ tự hàng đợi là FIFO - Nhập trước ra trước
Hoạt động
- Chèn - Chèn một phần tử vào hàng đợi.
- Xóa - Xóa một phần tử khỏi hàng đợi.
Điều kiện
-
Xếp hàng qua luồng - Cố gắng chèn một phần tử vào một hàng đợi đầy đủ.
-
Hàng đợi trong luồng - Đang cố gắng xóa một phần tử khỏi hàng đợi trống.
Thuật toán
Dưới đây là một thuật toán cho insert () -
- Kiểm tra lỗi tràn hàng đợi.
if (r==n)
printf ("Queue overflow") - Nếu không, hãy chèn một phần tử vào hàng đợi.
q[r] = item r++
Dưới đây là một thuật toán cho xóa () -
- Kiểm tra hàng đợi theo quy trình.
if (f==r)
printf ("Queue under flow") - Nếu không, hãy xóa một phần tử khỏi hàng đợi.
item = q[f] f++
Dưới đây là một thuật toán cho display () -
- Kiểm tra xem hàng đợi có trống hay không.
if (f==r)
printf("Queue is empty") - Nếu không, hãy in tất cả các phần tử từ ‘f’ đến ‘r’.
for(i=f; i<r; i++)
printf ("%d", q[i]); Chương trình
Sau đây là chương trình C để xóa một phần tử trong hàng đợi -
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 50
void insert();
int array[MAX];
int rear = - 1;
int front = - 1;
main(){
int add_item;
int choice;
while (1){
printf("1.Insert element to queue \n");
printf("2.Delete an element from queue\n");
printf("3.Display elements of queue \n");
printf("4.Quit \n");
printf("Enter your choice : ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice){
case 1:
insert();
break;
case 2:
delete();
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
printf("Wrong choice \n");
}
}
}
void insert(){
int add_item;
if (rear == MAX - 1)
printf("Queue Overflow \n");
else{
if (front == - 1)
/*If queue is initially empty */
front = 0;
printf("Inset the element in queue : ");
scanf("%d", &add_item);
rear = rear + 1;
array[rear] = add_item;
}
}
void display(){
int i;
if (front == - 1)
printf("Queue is empty \n");
else{
printf("Queue is : \n");
for (i = front; i <= rear; i++)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
void delete(){
if (front == - 1 || front > rear){
printf("Queue Underflow \n");
return ;
}
else{
printf("Element deleted from queue is : %d\n",array[front]);
front = front + 1;
}
} Đầu ra
Khi chương trình trên được thực thi, nó tạo ra kết quả sau -
1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 12 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 23 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 2 Element deleted from queue is: 12 Queue is: 23 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 2 Element deleted from queue is: 23 Queue is: 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 4
