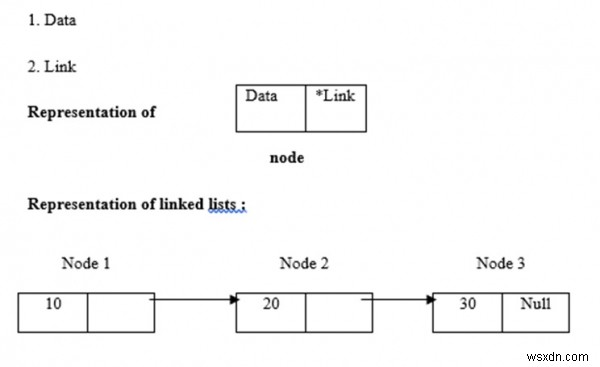
Danh sách được liên kết sử dụng phân bổ bộ nhớ động, tức là chúng phát triển và thu nhỏ tương ứng. Chúng được định nghĩa là một tập hợp các nút. Ở đây, các nút có hai phần, đó là dữ liệu và liên kết. Trình bày dữ liệu, liên kết và danh sách được liên kết được đưa ra dưới đây -
Hoạt động trên danh sách được liên kết
Có ba loại hoạt động trên danh sách được liên kết trong ngôn ngữ C, như sau -
- Chèn
- Xóa
- Chuyển hướng
Xóa
Hãy xem xét một ví dụ được đưa ra bên dưới -
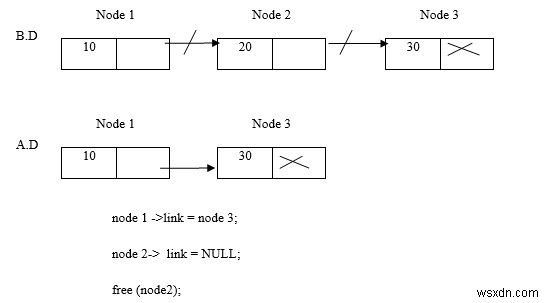
Xóa nút 2
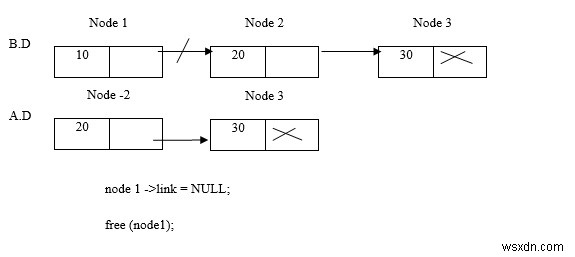
Xóa nút 1
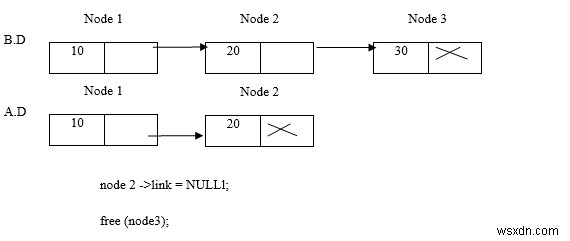
Xóa nút 3
Chương trình
Sau đây là chương trình C để xóa các phần tử trong danh sách được liên kết -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data){
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(struct Node **head_ref, int position){
//if list is empty
if (*head_ref == NULL)
return;
struct Node* temp = *head_ref;
if (position == 0){
*head_ref = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
for (int i=0; temp!=NULL && i<position-1; i++)
temp = temp->next;
if (temp == NULL || temp->next == NULL)
return;
struct Node *next = temp->next->next;
free(temp->next); // Free memory
temp->next = next;
}
void printList(struct Node *node){
while (node != NULL){
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main(){
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 8);
puts("Created List: ");
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 3);
puts("\n List after Deletion at position 3: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
Khi chương trình trên được thực thi, nó tạo ra kết quả sau -
Created List: 8 2 3 1 7 List after Deletion at position 3: 8 2 3 7
