Có thể tránh ngăn xếp chồng lên luồng và xếp chồng dưới luồng bằng cách cấp phát bộ nhớ động.
Các hoạt động được thực hiện dưới ngăn xếp trong ngôn ngữ lập trình C như sau -
- Đẩy
- Pop
Đẩy
Sau đây là cách triển khai cơ bản của danh sách được liên kết -
&item = 10 newnode = (node*) malloc (sizeof (node)); newnode ->data = item; newnode ->link = NULL; newnode ->link = start; start = newnode;
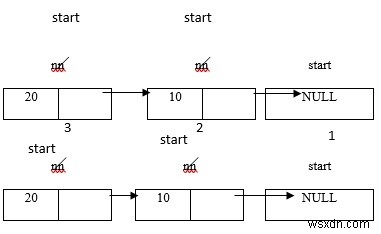
pop
Cú pháp như sau -
Cú pháp
if (start = = NULL)
printf("Deletion is not possible.List is empty")
else{
temp = start;
start = start link;
free (temp);
} Chương trình
Sau đây là chương trình C cho ngăn xếp bằng cách sử dụng danh sách được liên kết -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int info;
struct node *ptr;
}*top,*top1,*temp;
int topelement();
void push(int data);
void pop();
void empty();
void display();
void destroy();
void stack_count();
void create();
int count = 0;
void main(){
int no, ch, e;
printf("\n 1 - Push");
printf("\n 2 - Pop");
printf("\n 3 - Top");
printf("\n 4 - Empty");
printf("\n 5 - Exit");
printf("\n 6 - Display");
printf("\n 7 - Stack Count");
printf("\n 8 - Destroy stack");
create();
while (1){
printf("\n Enter choice : ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch (ch){
case 1:
printf("Enter element : ");
scanf("%d", &no);
push(no);
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
if (top == NULL)
printf("stack is empty");
else{
e = topelement();
printf("\n Top element : %d", e);
}
break;
case 4:
empty();
break;
case 5:
exit(0);
case 6:
display();
break;
case 7:
stack_count();
break;
case 8:
destroy();
break;
default :
printf(" wrong choice:Try again ");
break;
}
}
}
//empty stack
void create(){
top = NULL;
}
void stack_count(){
printf("\n no: of elements in stack : %d", count);
}
//push data
void push(int data){
if (top == NULL){
top =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
top->ptr = NULL;
top->info = data;
}
else{
temp =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
temp->ptr = top;
temp->info = data;
top = temp;
}
count++;
}
void display(){
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL){
printf("empty stack");
return;
}
while (top1 != NULL){
printf("%d ", top1->info);
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
}
void pop(){
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL){
printf("\n error");
return;
}
else
top1 = top1->ptr;
printf("\n Popped value : %d", top->info);
free(top);
top = top1;
count--;
}
int topelement(){
return(top->info);
}
//check stack empty or not
void empty(){
if (top == NULL)
printf("\n empty stack");
else
printf("\n stack not empty with %d values", count);
}
void destroy(){
top1 = top;
while (top1 != NULL){
top1 = top->ptr;
free(top);
top = top1;
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
free(top1);
top = NULL;
printf("\n all are destroyed");
count = 0;
} Đầu ra
Khi chương trình trên được thực thi, nó tạo ra kết quả sau -
1 - Push 2 - Pop 3 - Top 4 - Empty 5 - Exit 6 - Display 7 - Stack Count 8 - Destroy stack Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 23 Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 45 Enter choice: 1 Enter element: 56 Enter choice: 2 Popped value: 56 Enter choice: 6 45 23 Enter choice: 8 all are destroyed Enter choice: 6 empty stack Enter choice: 5
