Chúng tôi được cung cấp dữ liệu và mức độ ưu tiên dưới dạng giá trị số nguyên và nhiệm vụ là tạo một danh sách được liên kết theo mức độ ưu tiên đã cho và hiển thị kết quả.
Hàng đợi là một cấu trúc dữ liệu FIFO trong đó phần tử được chèn vào đầu tiên là phần tử đầu tiên bị xóa. Hàng đợi Ưu tiên là một loại hàng đợi trong đó các phần tử có thể được chèn hoặc xóa tùy thuộc vào mức độ ưu tiên. Nó có thể được thực hiện bằng cách sử dụng cấu trúc dữ liệu hàng đợi, ngăn xếp hoặc danh sách liên kết. Hàng đợi ưu tiên được triển khai bằng cách tuân theo các quy tắc sau -
- Dữ liệu hoặc phần tử có mức độ ưu tiên cao nhất sẽ được thực thi trước phần dữ liệu hoặc phần tử có mức độ ưu tiên thấp nhất.
- Nếu hai phần tử có cùng mức độ ưu tiên, chúng sẽ được thực thi theo trình tự mà chúng được thêm vào danh sách.
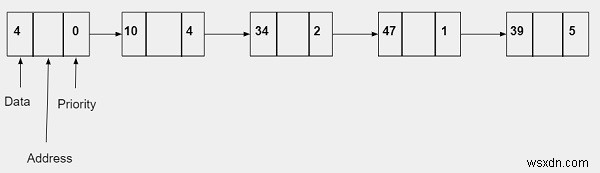
Một nút của danh sách được liên kết để triển khai hàng đợi ưu tiên sẽ chứa ba phần -
- Dữ liệu - Nó sẽ lưu trữ giá trị số nguyên.
- Địa chỉ - Nó sẽ lưu trữ địa chỉ của nút tiếp theo
- Mức độ ưu tiên − Nó sẽ lưu trữ mức độ ưu tiên là một giá trị số nguyên. Nó có thể nằm trong khoảng từ 0-10 trong đó 0 đại diện cho mức độ ưu tiên cao nhất và 10 đại diện cho mức độ ưu tiên thấp nhất.
Ví dụ
Đầu vào
Đầu ra

Thuật toán
Start Step 1-> Declare a struct node Declare data, priority Declare a struct node* next Step 2-> In function Node* newNode(int d, int p) Set Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)) Set temp->data = d Set temp->priority = p Set temp->next = NULL Return temp Step 3-> In function int peek(Node** head) return (*head)->data Step 4-> In function void pop(Node** head) Set Node* temp = *head Set (*head) = (*head)->next free(temp) Step 5-> In function push(Node** head, int d, int p) Set Node* start = (*head) Set Node* temp = newNode(d, p) If (*head)->priority > p then, Set temp->next = *head Set (*head) = temp Else Loop While start->next != NULL && start->next->priority < p Set start = start->next Set temp->next = start->next Set start->next = temp Step 6-> In function int isEmpty(Node** head) Return (*head) == NULL Step 7-> In function int main() Set Node* pq = newNode(7, 1) Call function push(&pq, 1, 2) Call function push(&pq, 3, 3) Call function push(&pq, 2, 0) Loop While (!isEmpty(&pq)) Print the results obtained from peek(&pq) Call function pop(&pq) Stop
Ví dụ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// priority Node
typedef struct node {
int data;
int priority;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int d, int p) {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = d;
temp->priority = p;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
int peek(Node** head) {
return (*head)->data;
}
void pop(Node** head) {
Node* temp = *head;
(*head) = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
void push(Node** head, int d, int p) {
Node* start = (*head);
Node* temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((*head)->priority > p) {
temp->next = *head;
(*head) = temp;
} else {
while (start->next != NULL &&
start->next->priority < p) {
start = start->next;
}
// Either at the ends of the list
// or at required position
temp->next = start->next;
start->next = temp;
}
}
// Function to check the queue is empty
int isEmpty(Node** head) {
return (*head) == NULL;
}
// main function
int main() {
Node* pq = newNode(7, 1);
push(&pq, 1, 2);
push(&pq, 3, 3);
push(&pq, 2, 0);
while (!isEmpty(&pq)) {
printf("%d ", peek(&pq));
pop(&pq);
}
return 0;
} Đầu ra
2 7 1 3
