Danh sách được liên kết sử dụng phân bổ bộ nhớ động và là tập hợp các nút.
Các nút có hai phần là dữ liệu và liên kết.
Các loại danh sách được liên kết
Các loại danh sách liên kết trong ngôn ngữ lập trình C như sau -
- Danh sách được liên kết đơn / lẻ.
- Danh sách được liên kết đôi / liên kết đôi.
- Danh sách liên kết đơn hình tròn.
- Danh sách liên kết kép hình tròn.
Danh sách liên kết đôi
Sơ đồ dưới đây mô tả sự biểu diễn của danh sách liên kết kép.
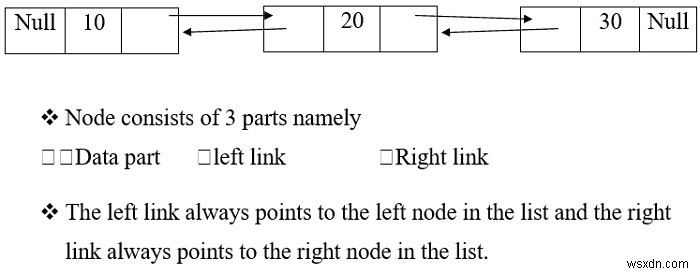
Ví dụ
Sau đây là chương trình C để chèn một nút ở bất kỳ vị trí nào bằng cách sử dụng danh sách liên kết đôi -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int num;
struct node * preptr;
struct node * nextptr;
}*stnode, *ennode;
void DlListcreation(int n);
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(int num);
void DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num);
void DlLinsertNodeAtAny(int num, int pos);
void displayDlList(int a);
int main(){
int n,num1,a,insPlc;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
printf("\n\n Doubly Linked List : Insert a node at any position :\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf(" Input the number of nodes : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
DlListcreation(n);
a=1;
displayDlList(a);
printf(" Input the position ( 1 to %d ) to insert a new node : ",n+1);
scanf("%d", &insPlc);
printf(" Input data for the position %d : ", insPlc);
scanf("%d", &num1);
DlLinsertNodeAtAny(num1,insPlc);
a=2;
displayDlList(a);
return 0;
}
void DlListcreation(int n){
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if(n >= 1){
stnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(stnode != NULL){
printf(" Input data for node 1 : "); // assigning data in the first node
scanf("%d", &num);
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
for(i=2; i<=n; i++){
fnNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(fnNode != NULL){
printf(" Input data for node %d : ", i);
scanf("%d", &num);
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode;
fnNode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode->nextptr = fnNode;
ennode = fnNode;
}
else{
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
break;
}
}
}
else{
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtAny(int num, int pos){
int i;
struct node * newnode, *tmp;
if(ennode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!\n");
}
else{
tmp = stnode;
i=1;
while(i<pos-1 && tmp!=NULL){
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
i++;
}
if(pos == 1){
DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(num);
}
else if(tmp == ennode){
DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(num);
}
else if(tmp!=NULL){
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = tmp->nextptr;
newnode->preptr = tmp;
if(tmp->nextptr != NULL){
tmp->nextptr->preptr = newnode; // n+1th node is linking with new node
}
tmp->nextptr = newnode; // n-1th node is linking with new node
}
else{
printf(" The position you entered, is invalid.\n");
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning(int num){
struct node * newnode;
if(stnode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!\n");
}
else{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = stnode;
newnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->preptr = newnode;
stnode = newnode;
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtEnd(int num){
struct node * newnode;
if(ennode == NULL){
printf(" No data found in the list!\n");
}
else{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = NULL;
newnode->preptr = ennode;
ennode->nextptr = newnode;
ennode = newnode;
}
}
void displayDlList(int m){
struct node * tmp;
int n = 1;
if(stnode == NULL) {
printf(" No data found in the List yet.");
}
else{
tmp = stnode;
if (m==1) {
printf("\n Data entered in the list are :\n");
}
else{
printf("\n After insertion the new list are :\n");
}
while(tmp != NULL){
printf(" node %d : %d\n", n, tmp->num);
n++;
tmp = tmp->nextptr; // current pointer moves to the next node
}
}
} Đầu ra
Khi chương trình trên được thực thi, nó tạo ra kết quả sau -
Doubly Linked List : Insert node at any position: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Input the number of nodes : 5 Input data for node 1 : 23 Input data for node 2 : 12 Input data for node 3 : 11 Input data for node 4 : 34 Input data for node 5 : 10 Data entered in the list are : node 1 : 23 node 2 : 12 node 3 : 11 node 4 : 34 node 5 : 10 Input the position ( 1 to 6 ) to insert a new node : 5 Input data for the position 5 : 78 After insertion the new list are : node 1 : 23 node 2 : 12 node 3 : 11 node 4 : 34 node 5 : 78 node 6 : 10
