WordPress của bạn có bị tấn công không? Hay bạn nghi ngờ có điều gì đó không ổn với trang web của mình?
Điều đầu tiên bạn nên làm nếu bạn nghi ngờ rằng WordPress của mình bị tấn công là quét trang web của bạn.
Điều này sẽ xác nhận những nghi ngờ của bạn về vụ hack và giúp bạn quyết định cách hành động tốt nhất để đưa trang web của bạn trở lại trạng thái tốt.
Chúng tôi nhận được email mỗi ngày từ quản trị viên trang web, những người đang hoảng sợ về các trang web WordPress bị tấn công. Một số người trong số họ đã mất quyền truy cập vào trang web của họ do máy chủ web tạm ngưng tài khoản của họ. Và một số đã mất hoàn toàn quyền truy cập vào wp-admin.
Khi bạn đã xác nhận bị hack trên trang web WordPress của mình, bạn cần phải Cài đặt MalCare và dọn dẹp trang web của mình ngay lập tức.
Hướng dẫn từng bước này sẽ giúp bạn xác định nguyên nhân của vụ tấn công và bảo vệ trang web của bạn khỏi bất kỳ mối đe dọa hiện tại hoặc trong tương lai.
WordPress có một cộng đồng lớn mạnh với vô số tài nguyên, nhưng hầu hết các giải pháp bạn thấy đều khó thực hiện. Vì vậy, những lời khuyên xấu thường dẫn đến tác hại nhiều hơn lợi ích. Điều này có thể cực kỳ bực bội và căng thẳng khi trải qua, và sau đó bạn có thể cảm thấy như tin tặc đã thắng và công việc của bạn bị mất. Đây không phải là trường hợp.
Nếu bạn cho rằng trang web WordPress của mình đã bị tấn công, chúng tôi sẽ giúp bạn sửa chữa nó.
Điều quan trọng cần nhớ là các vụ hack có thể được giải quyết. Chúng tôi đã làm sạch hơn 20.000 trang web WordPress và bảo vệ hơn 100.000 trang web hàng ngày. Chúng tôi đã đúc kết sự khôn ngoan này thành hướng dẫn sau đây sẽ giúp bạn xác thực việc hack, dọn dẹp trang web của bạn và bảo vệ nó trong tương lai.
TL; DR:Dọn dẹp trang web WordPress bị tấn công của bạn trong 5 phút. Không nên coi nhẹ các tin tặc, vì chúng gây ra thiệt hại theo cấp số nhân nếu chúng không được khắc phục lâu hơn. MalCare giúp bạn loại bỏ mọi dấu vết của phần mềm độc hại khỏi trang web của bạn bằng cách nhấp vào nút.
Làm cách nào để loại bỏ hack khỏi trang web WordPress của bạn một cách nhanh chóng?
Một trang web WordPress bị tấn công có thể là nguyên nhân gây ra sự hoảng sợ hoặc thất vọng. Nhưng đừng lo lắng, cho dù vụ tấn công có tồi tệ đến đâu, chúng tôi vẫn có thể giúp bạn khắc phục một trang web WordPress bị tấn công.
Các triệu chứng của phần mềm độc hại trên trang web của bạn
Phần mềm độc hại gây hiểu lầm và nó có thể che giấu bạn vì đó là cách nó được thiết kế. Vì vậy rất khó để xác định xem trang WordPress của bạn có dính phần mềm độc hại hay không. Nhưng có một số triệu chứng mà bạn có thể để ý. Dưới đây là một số triệu chứng cần chú ý, có thể là dấu hiệu của phần mềm độc hại trên trang web của bạn:
- Spam trong kết quả tìm kiếm của Google
- Sự cố trên trang web của bạn
- Thay đổi phụ trợ đối với trang web
- Sự cố máy chủ web
- Vấn đề về hiệu suất
- Các vấn đề về trải nghiệm người dùng
- Những thay đổi trong các mẫu phân tích
Chúng tôi đã giải thích những vấn đề này một cách chi tiết trong các phần sau của bài viết này nếu bạn muốn hiểu rõ hơn về chúng.
Làm cách nào để quét phần mềm độc hại trên trang web của bạn?
Bây giờ bạn đã biết những gì cần chú ý, nếu bạn nghi ngờ bị hack WordPress, điều đầu tiên cần làm là quét trang web của bạn.
Có ba cách để bạn có thể quét trang web của mình để tìm kiếm các vụ tấn công. Mỗi cách này đều có ưu và nhược điểm của nó. Trước khi chọn một, chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên đọc chi tiết phần liên quan để xem phần nào phù hợp với yêu cầu của bạn.
- Quét sâu bằng máy quét bảo mật
- Quét bằng máy quét trực tuyến
- Quét phần mềm độc hại theo cách thủ công
Chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên quét bằng máy quét bảo mật như MalCare, vì MalCare được xây dựng đặc biệt để tìm ra phần mềm độc hại ẩn mà không dễ tìm thấy bằng các phương pháp khác.
Làm cách nào để xóa trang web WordPress bị tấn công của bạn?
Bây giờ bạn đã xác nhận bị hack trên trang web của mình, đã đến lúc khắc phục trang web WordPress bị tấn công. Có nhiều cách khác nhau để làm sạch trang web của bạn, nhưng chúng tôi thực sự khuyên bạn nên sử dụng một plugin bảo mật tốt như MalCare. MalCare cho phép bạn tự động dọn dẹp trang web của mình trong vòng vài phút và không tính phí mỗi lần dọn dẹp. Nó cũng sẽ bảo vệ trang web WordPress của bạn không bị tấn công trong tương lai.
Ngoài ra, chúng tôi đã đưa vào phần làm sạch thủ công trong bài viết dưới đây. Tuy nhiên, trừ khi bạn là chuyên gia bảo mật, chúng tôi không khuyên bạn nên làm sạch thủ công vì nó có thể dẫn đến nhiều vấn đề hơn bạn đã gặp.
- Sử dụng một plugin bảo mật để làm sạch vụ hack
- Thuê một chuyên gia bảo mật WordPress
- Làm sạch bản hack WordPress theo cách thủ công
Bạn có thể xem qua các phần này trong bài viết để tìm ra cái nào phù hợp với bạn nhất. Nhưng trừ khi bạn là một chuyên gia bảo mật, chúng tôi không khuyên bạn nên làm sạch trang web WordPress bị tấn công theo cách thủ công vì nó có thể dẫn đến nhiều vấn đề hơn bạn đã gặp phải.
Làm cách nào để khắc phục thiệt hại do hack WordPress?
Có một số vấn đề xảy ra khi trang web WordPress của bạn bị tấn công. Trang web của bạn có thể đã bị đưa vào danh sách đen hoặc bạn có thể đã mất quyền truy cập vào nó. Để trang web của bạn hoạt động trở lại, có một số điều bạn cần làm.
- Lấy lại quyền truy cập vào trang web
- Xóa trang web của bạn khỏi danh sách đen của Google
- Kiểm soát thiệt hại thương hiệu
Làm cách nào để bảo vệ trang web WordPress của bạn không bị tấn công trong tương lai?
Cuối cùng, khi trang web WordPress của bạn đã sạch, chúng tôi cũng đã bao gồm một phần về bảo mật trang web. Bạn sẽ tìm thấy các mẹo và thông tin về
- Cách tránh bị tấn công trong tương lai
- Nếu WordPress dễ bị tấn công
- Cách hack hoạt động
- Hậu quả của một trang web bị tấn công là gì
- Tại sao các trang web WordPress bị tấn công.
Với tất cả các phần này, chúng tôi đã đề cập đến hướng dẫn đầy đủ để vượt qua một cuộc tấn công WordPress và bảo vệ trang web WordPress của bạn không bị tấn công trong tương lai. Vì vậy, nếu bạn bị hack, đừng lo lắng. Chúng tôi đã hỗ trợ bạn!
Việc WordPress của bạn bị tấn công có nghĩa là gì?
Trang web WordPress bị tấn công có nghĩa là trang web của bạn hiện có mã độc. Vì có nhiều loại hack WordPress khác nhau, phần mềm độc hại có thể ở bất kỳ vị trí nào, có nhiều biến thể và có thể biểu hiện theo nhiều cách khác nhau. Ví dụ:một trong những biến thể của hack chuyển hướng WordPress lây nhiễm vào từng bài đăng trên một trang web — ngay cả khi có hàng trăm bài đăng.
Tin tặc và phần mềm độc hại gây ra hàng triệu thiệt hại cho các doanh nghiệp và cá nhân, làm trật bánh không chỉ các trang web và trải nghiệm người dùng mà còn cả thứ hạng SEO, gây ra các vấn đề pháp lý. Chưa kể đến sự căng thẳng vô cùng của việc hồi phục. Phần mềm độc hại tạo ra các cửa hậu, vì vậy ngay cả khi bạn tìm thấy và loại bỏ mã xấu, trang web WordPress của bạn vẫn bị tấn công.
Điều quan trọng cần nhớ là nó đã đủ tệ để bị tấn công, nhưng nó sẽ trở nên tồi tệ hơn theo cấp số nhân theo thời gian. Phần mềm độc hại còn lại trên trang web của bạn càng lâu, nó sẽ tự tái tạo, gây ra nhiều thiệt hại hơn và sử dụng trang web của bạn để lây nhiễm các trang web khác. Trên thực tế, nếu máy chủ web của bạn chưa tạm ngưng tài khoản của bạn, nó có thể sẽ xảy ra. Với Google cũng vậy. Quét và làm sạch trang web của bạn trong vài phút, và giúp bạn tiết kiệm rất nhiều sự đau buồn này.
Làm thế nào để biết liệu trang web WordPress của bạn có bị tấn công hay không?
Rắc rối với các bản hack WordPress là chúng không thể đoán trước được — hay đúng hơn là chúng được thiết kế để không thể đoán trước được. Tin tặc muốn gây nhầm lẫn cho quản trị viên, nhằm khai thác càng nhiều càng tốt từ các trang web càng lâu càng tốt. Do đó, phần mềm độc hại có thể làm cho các trang web hoạt động kỳ lạ, nhưng không nhất thiết phải luôn luôn.
Ví dụ:quản trị viên thấy một triệu chứng giống như một chuyển hướng độc hại một lần và sau đó không bao giờ thấy nó nữa. Điều tương tự cũng xảy ra với quảng cáo độc hại, trong đó quảng cáo cho các sản phẩm và dịch vụ spam xuất hiện giữa các quảng cáo hoàn toàn lành tính và hợp pháp trên trang web của bạn. Tin tặc thiết lập một cookie để quản trị viên trang web bị ru ngủ trong cảm giác an toàn sai lầm. Theo đúng nghĩa đen.
Tuy nhiên, nếu máy chủ lưu trữ web của bạn đã tạm ngưng tài khoản của bạn hoặc khách truy cập của bạn nhìn thấy cảnh báo danh sách đen của Google khi họ cố gắng truy cập trang web của bạn, thì đây là những dấu hiệu khá đáng tin cậy cho thấy trang web WordPress của bạn đã bị tấn công.
Mẹo: Khi gặp phải phần mềm độc hại hoặc các triệu chứng trên trang web của bạn, bạn nên ghi lại tất cả các biến số:hệ điều hành, trình duyệt, thiết bị, các bước trước đó, v.v. Điều này sẽ giúp giải quyết vấn đề, cho dù bạn đang tìm kiếm sự trợ giúp của chuyên gia hay đang cố gắng tự làm sạch phần mềm độc hại.
A. Các triệu chứng của một trang web WordPress bị tấn công
Mỗi bản hack WordPress được cấu trúc khác nhau và do đó biểu hiện theo những cách khác nhau. Một cuộc tấn công đưa vào liên kết thư rác sẽ không giống như một cuộc tấn công thực thi mã từ xa. Vì vậy, bạn sẽ không thấy tất cả các triệu chứng dưới đây nhưng có thể gặp một hoặc hai.
Chúng tôi đã tổng hợp danh sách toàn diện này về các triệu chứng trang web WordPress bị tấn công và sắp xếp theo vị trí các triệu chứng có thể nhìn thấy.
1. Spam hiển thị trong kết quả tìm kiếm của Google
Bạn đã dành thời gian và năng lượng làm việc cho SEO để trang web của bạn có thứ hạng trong các tìm kiếm từ khóa. Chúng tôi đặt điều này ở đầu danh sách vì phần mềm độc hại thường chỉ hiển thị với Google.
- Mô tả meta rác: Các trang web có mô tả meta theo ngữ cảnh ám chỉ đến nội dung của trang cụ thể đó. Các bản hack WordPress sẽ hiển thị ở đây dưới dạng các ký tự tiếng Nhật, các chuỗi từ khóa không liên quan hoặc các giá trị rác.
- Kết quả cho các trang bạn không tạo nhưng có trên trang web của bạn: Đây là một cảm giác đặc biệt khó hiểu, bởi vì nếu ai đó tìm kiếm một từ khóa xếp hạng, trang web của bạn sẽ hiển thị các trang bổ sung và bất ngờ này trong kết quả.
- Danh sách đen của Google: Khi khách truy cập nhấp vào trang web của bạn từ kết quả tìm kiếm, Google sẽ đưa ra một cảnh báo màu đỏ lớn cho khách truy cập biết rằng trang web của bạn có chứa phần mềm độc hại và không an toàn. Đây là một phần trong sáng kiến Duyệt web an toàn của họ và các công cụ tìm kiếm khác cũng sử dụng nó để bảo vệ người dùng của họ.
- Thông báo ‘Trang web có thể bị tấn công’: Phiên bản thu nhỏ của danh sách đen của Google là thấy thông báo "Trang web có thể bị tấn công" bên dưới tiêu đề trang web của bạn trong kết quả tìm kiếm.

2. Sự cố trên trang web của bạn
WordPress Hacks có thể hiển thị trực tiếp trên trang web của bạn để mọi người có thể xem. Những điều này thường là do tin tặc muốn phá hoại trang web hoặc gây ra một cuộc tấn công kỹ thuật xã hội, chẳng hạn như lừa đảo.
Bạn có thể thấy các trang này nếu bạn đăng nhập với tư cách là quản trị viên hoặc người dùng, nhưng nếu bạn thấy các trang hoặc bài đăng mà bạn không tạo, rất có thể chúng sẽ trông giống như một trong những trang sau:
- Trang spam :Các trang spam trên trang web của bạn hầu hết là các trang giống nhau hiển thị trong kết quả tìm kiếm. Các trang spam được chèn vào các trang web được xếp hạng để tạo liên kết đến cho các trang web khác. Đây là một cách chơi cho SEO và kết quả là nâng cao thứ hạng của trang web đích.
- Cửa sổ bật lên spam: Như tên cho thấy, đây là các cửa sổ bật lên trên trang web của bạn là spam và có ý định khiến người dùng tải xuống phần mềm độc hại hoặc đưa họ đến một trang web khác một cách gian lận. Cửa sổ bật lên có thể được tạo ra do phần mềm độc hại hoặc thậm chí quảng cáo mà bạn đã bật trên trang web của mình qua mạng quảng cáo. Các mạng quảng cáo nói chung có các chính sách bảo mật liên quan đến nội dung của nhà quảng cáo, nhưng phần mềm độc hại kỳ lạ vẫn có thể xâm nhập bất ngờ.
- Chuyển hướng tự động đến các trang web khác: Triệu chứng này khiến người dùng của chúng tôi căng thẳng tối đa, bởi vì không chỉ các bài đăng và trang chuyển hướng mà đôi khi ngay cả trang đăng nhập wp cũng vậy. Điều này có nghĩa là họ thậm chí không thể ở lại trang web của mình đủ lâu để xem điều gì không ổn. Do đó, chúng tôi có toàn bộ bài viết dành riêng cho chuyển hướng tự động và cách khắc phục chúng.
- Trang lừa đảo: Lừa đảo là một loại tấn công kỹ thuật xã hội, lừa mọi người sẵn sàng chia sẻ dữ liệu của họ bằng cách giả mạo là một trang web hoặc dịch vụ hợp pháp, đặc biệt là các ngân hàng. Thông thường, khi nhìn thấy các trang lừa đảo trên trang web của khách hàng, chúng tôi đã nhận thấy các tệp hình ảnh biểu trưng ngân hàng trong mã.
- Các trang bị hỏng một phần: Bạn có thể thấy mã ở đầu hoặc cuối một số trang trên trang web của mình. Thoạt nhìn, nó có vẻ giống như một lỗi mã và đôi khi nó có thể là kết quả của một plugin hoặc chủ đề bị trục trặc. Nhưng nó cũng có thể báo hiệu sự hiện diện của phần mềm độc hại.
- Màn hình chết chóc màu trắng: Bạn truy cập trang web của mình và trình duyệt của bạn bị trống. Không có thông báo lỗi, không có gì. Không có gì để tương tác hoặc sửa chữa và do đó không có manh mối nào về những gì đã xảy ra với trang web.

3. Các thay đổi đối với phần phụ trợ của trang web WordPress của bạn
Những thay đổi này thường bị quản trị viên trang web bỏ qua trừ khi họ quá tò mò hoặc đã cài đặt nhật ký hoạt động.
- Các thay đổi đối với mã trang web của bạn: Trang web WordPress của bạn được xây dựng bằng mã, vì vậy những thay đổi này có thể nằm trong các tệp, plugin hoặc chủ đề cốt lõi của WordPress. Về cơ bản, phần mềm độc hại có thể ở bất cứ đâu.
- Những thay đổi không mong muốn đối với hoàn toàn các bài đăng và trang hoặc các trang mới: Các bài đăng và trang được thêm vào hoặc các thay đổi được thực hiện đối với những bài hiện có. Nhiều khách hàng cho biết họ đã nhìn thấy những thay đổi này, mặc dù họ là những người duy nhất quản lý nội dung trang web. Các trang mới có khả năng hiển thị trong bất kỳ thứ gì lập chỉ mục trang web của bạn, bao gồm kết quả tìm kiếm của Google, số liệu phân tích và sơ đồ trang web của bạn.
- Người dùng không mong muốn có đặc quyền quản trị: Trong một số trường hợp, quản trị viên trang web đã nhận được email về các tài khoản mới được tạo trên trang web của họ. Các tài khoản thường có tên hoặc địa chỉ email vô nghĩa, chủ yếu là cả hai. Họ đã được cảnh báo về hoạt động bất thường này vì họ đã bật cài đặt thông báo cho họ về việc tạo tài khoản mới.
- Cài đặt đã được thay đổi: Tất nhiên, mỗi trang web được thiết lập khác nhau, vì vậy triệu chứng này sẽ khác nhau giữa các trang web. Trong một số trường hợp, người dùng báo cáo rằng cài đặt tạo tài khoản đã thay đổi, trong khi những người khác cho biết tệp index.php của họ khác. Mỗi lần quản trị viên cố gắng hoàn nguyên nó về trạng thái ban đầu, các cài đặt lại được thay đổi ngay lập tức.
- Plugin giả mạo: Rất nhiều phần mềm độc hại được giấu khéo léo trong các thư mục và tệp có vẻ hợp pháp. Các plugin giả mạo bắt chước kiểu dáng của các plugin thực, nhưng có rất ít tệp trong đó hoặc có tên lạ thường không tuân theo quy ước đặt tên. Đây không phải là một chẩn đoán chắc chắn, nhưng nó là một nguyên tắc cơ bản để xác định.
4. Máy chủ lưu trữ web gắn cờ các vấn đề với trang web của bạn
Máy chủ lưu trữ web của bạn đặc biệt được đầu tư vào việc đảm bảo trang web của bạn không có phần mềm độc hại vì phần mềm độc hại trên máy chủ của họ gây ra các vấn đề lớn. Hầu hết các máy chủ web tốt thường xuyên quét các trang web và thông báo cho người dùng về phần mềm độc hại trên trang web của họ.
- Đặt trang web của bạn ngoại tuyến: Nếu máy chủ lưu trữ web của bạn đã tạm ngưng tài khoản của bạn hoặc đưa trang web của bạn vào trạng thái ngoại tuyến, thì đây là dấu hiệu đầu tiên có gì đó không ổn. Mặc dù máy chủ web cũng sẽ tạm ngưng trang web của bạn do vi phạm chính sách hoặc do hóa đơn chưa thanh toán, phần mềm độc hại là lý do chính cho động thái này. Luôn luôn, họ sẽ liên hệ qua email với lý do của họ. Trong trường hợp họ đã phát hiện ra phần mềm độc hại, bạn nên hỏi danh sách các tệp bị tấn công mà máy quét của họ đã phát hiện được và yêu cầu họ đưa các IP vào danh sách trắng để bạn có thể truy cập trang web của mình để xóa chúng.
- Sử dụng máy chủ quá mức: Trong trường hợp này, bạn nhận được email từ công ty lưu trữ web thông báo rằng trang web của bạn đã vượt quá hoặc sắp đạt đến giới hạn kế hoạch. Một lần nữa, đây không phải là một triệu chứng kết luận, bởi vì bạn có thể thấy lưu lượng truy cập tăng đột biến do các lý do khác, chẳng hạn như chiến dịch hoặc quảng cáo. Hoặc có lẽ có một lý do thời sự. Tuy nhiên, các cuộc tấn công và hack bằng bot tiêu tốn rất nhiều tài nguyên máy chủ, vì vậy tốt nhất là bạn nên điều tra nếu bạn thấy mức sử dụng tài nguyên máy chủ tăng đột biến không mong muốn.
5. Vấn đề về hiệu suất
Phần mềm độc hại có thể khiến hàng loạt thứ bị phá hủy trong trang web. Như chúng tôi đã nói trước đây, đôi khi các triệu chứng là vô hình hoặc không rõ ràng, giống như một trang mới hoặc người dùng mới.
- Trang web trở nên chậm chạp
- Trang web không thể truy cập được , bởi vì tài nguyên máy chủ đã được sử dụng hết, vì vậy khách truy cập của bạn sẽ thấy lỗi 503 hoặc 504. Có những cách khác mà một trang web có thể không truy cập được, chẳng hạn như chặn địa lý hoặc các thay đổi đối với tệp .htaccess.
6. Sự cố trải nghiệm người dùng
Quản trị viên đôi khi là những người cuối cùng phát hiện ra các vụ hack vì tin tặc có thể ẩn các triệu chứng khỏi người dùng đã đăng nhập. Nhấp để Tweet
Tuy nhiên, khách truy cập vẫn thấy các triệu chứng, đây là một trải nghiệm tồi tệ và có tác động tiêu cực đến thương hiệu của bạn.
- Người dùng không thể đăng nhập vào trang web của bạn
- Khách truy cập được chuyển hướng từ trang web của bạn
- Email từ trang web đi vào thư mục spam
- Khách truy cập phàn nàn về việc nhìn thấy các triệu chứng phần mềm độc hại, như cửa sổ bật lên hoặc các trang lừa đảo
7. Hành vi không mong muốn trong phân tích
Phân tích là nguồn chân lý của nhiều thứ và dấu hiệu nhiễm phần mềm độc hại chỉ xảy ra là một trong những điều đó.
- Bảng điều khiển tìm kiếm gắn cờ các vấn đề bảo mật: Google Search Console quét giao diện người dùng trang web của bạn, giống như một trình quét giao diện người dùng và có thể tìm thấy phần mềm độc hại. Bạn sẽ thấy cảnh báo trên trang tổng quan của mình hoặc xem các trang bị gắn cờ trong tab Vấn đề bảo mật.
- Lưu lượng truy cập tăng từ các quốc gia nhất định: Lưu lượng truy cập tăng có thể là dấu hiệu của phần mềm độc hại, nếu chúng không mong muốn. Google Analytics vẫn lọc ra hầu hết lưu lượng truy cập bot, nhưng đôi khi, người dùng thấy mức tăng đột biến từ các quốc gia cụ thể. Triệu chứng này thường rõ ràng hơn đối với một trang web có liên quan tại địa phương.

Có một khả năng nhỏ là trang web của bạn có thể bị trục trặc do bản cập nhật bị lỗi hoặc sự cố máy chủ hoặc thậm chí là lỗi mã hóa. Tuy nhiên, nếu bạn thấy nhiều hơn một trong số này, rất có thể trang web của bạn đã bị tấn công.
Một số điểm chính cần nhớ
- Tin tặc muốn phần mềm độc hại không bị phát hiện càng lâu càng tốt, vì vậy rất nhiều triệu chứng được ngụy trang từ quản trị viên trang web và / hoặc người dùng đã đăng nhập
- Một số có thể hiển thị mọi lúc; một số có thể thỉnh thoảng xảy ra / không nhất quán
- Một số bản hack hoàn toàn ẩn đối với mọi người; tùy thuộc vào phần mềm độc hại
- Một số phần mềm độc hại sẽ chỉ xuất hiện với Google chứ không xuất hiện với ai khác
B. Quét trang web WordPress của bạn để tìm hack
Ngay cả khi bạn đã thấy một số triệu chứng của trang web WordPress bị tấn công từ danh sách ở trên, chúng không phải là dấu hiệu kết luận của một cuộc tấn công. Cách duy nhất để biết liệu WordPress của bạn có bị tấn công hay không là để quét trang web của bạn.
1. Quét sâu trang web của bạn bằng plugin bảo mật
Quét trang web của bạn miễn phí với MalCare để xác nhận xem WordPress của bạn có bị tấn công hay không. Bạn sẽ có câu trả lời rõ ràng về phần mềm độc hại trên trang web của mình.

Chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên sử dụng MalCare vì một số lý do, nhưng chủ yếu là vì chúng tôi đã xem và xử lý hàng trăm vụ tấn công từ các trang web. Quản trị viên trang web Panicking gửi email cho chúng tôi hàng tuần vì họ không thể đăng nhập vào trang web của họ hoặc máy chủ web của họ đã tạm ngưng tài khoản của họ do phần mềm độc hại được phát hiện.
Máy quét của MalCare được sử dụng hoàn toàn miễn phí. Khi bạn đã có báo cáo kết luận về việc liệu trang web WordPress của mình có bị xâm phạm hay không, khi đó bạn có thể nâng cấp để sử dụng tính năng tự động làm sạch để loại bỏ phần mềm độc hại ngay lập tức khỏi tệp và cơ sở dữ liệu.
Các plugin bảo mật khác sử dụng đối sánh tệp để xác định phần mềm độc hại. Đó là một cơ chế không hoàn hảo và dẫn đến kết quả dương tính giả và các vấn đề phần mềm độc hại bị bỏ sót. Không cần đi quá sâu vào các kỹ thuật, nếu phần mềm độc hại có một biến thể mới, rõ ràng sẽ không có trong các danh sách phù hợp này, thì cơ chế sẽ không thành công ngay tại đó. Đây chỉ là một trong những cách mà nó không thành công. Ngoài ra, các plugin sử dụng tài nguyên của trang web để chạy các quá trình quét này. Điều này làm chậm trang web đáng kể.
MalCare không dựa vào đối sánh tệp để xác định phần mềm độc hại nhưng có một thuật toán phức tạp kiểm tra mã cho hơn 100 đặc điểm trước khi cho là an toàn hoặc nguy hiểm.
2. Quét bằng máy quét bảo mật trực tuyến
Giải pháp thay thế thứ hai để quét trang web của bạn là sử dụng máy quét bảo mật trực tuyến. Hãy nhớ rằng tất cả các trình quét không được xây dựng giống nhau và các trình quét bảo mật trực tuyến nhất thiết phải kém hiệu quả hơn các plugin bảo mật.
Mọi người có thể phản đối việc thêm một plugin bảo mật để quét trang web của họ, nhưng mấu chốt ở đây là. Máy quét giao diện người dùng chỉ có quyền truy cập vào các phần hiển thị công khai trên trang web của bạn. Việc mã không được hiển thị công khai là một điều tốt vì bạn không muốn các tệp cấu hình của mình hiển thị với mọi người trên Internet.
Unfortunately though, malware is not considerate enough to only attack publicly visible files. It can hide anywhere, and in fact, will hide in places that frontend scanners cannot reach. That’s why site-level scanners are most effective.
Our advice is to use an online security scanner as the first line of diagnostics. If it turns out positive, that’s a good starting point to move to clean hacked WordPress website. However, a word of caution:do not rely exclusively on lists of hacked files that the scanner gives you. Those are just the ones that the scanner was able to flag. There are potentially many, many more instances of the malicious code.
3. Scan for malware manually
Although we are including this section in the article, we strongly advise against anyone attempting to deal with malware manually—scanning or cleaning.
A good security plugin, like MalCare, is really the way to go, because it will do everything that’s in this section, but faster and better. Remember that the WordPress hack is getting worse the longer it is left unattended.
Scanning your hacked WordPress site for malware essentially means looking for junk code in files and the database. We are aware that ‘junk code’ means very little in terms of guidance, but hacks come in different forms. They each look and behave differently.
We have provided code examples of hacks in a later section, but we must stress that they are indicative only.
If you are opting to manually scan your website for malicious code, check for recently modified files , and make sure to look in both the files and the database. A word of caution here:update times can also be changed. A clever hacker can set the updated timestamp to something entirely different.
Tip: Keep a log of your actions when scanning your website. It helps in the debugging process later on, in case your website only behaves oddly when accessed by mobile for instance. Or if you see a suspicious-looking script tag in one of the files.
C. Other diagnostic steps to check for malware
There are a few other checks that you can use to determine if your WordPress site has been hacked. Some of these overlap slightly with the symptoms listed above, but we are including them here on the off chance that the symptom didn’t appear organically.
1. Log in from an incognito browser
If you see a symptom once, like a redirect, but cannot replicate it, then try logging in from a different computer or an incognito browser. Hackers set cookies to create the illusion that any anomalies you see on your website are just that:anomalies, and not signs of hacks.
Try Googling your website and clicking through from there. Does your website load correctly? How about if you put the URL directly in the browser? What happens then?
We mentioned this before, but do keep notes of what you did to replicate the symptoms. Did you log in from a mobile device, or are you clicking through from Google search results? These clues help identify the hack location to some extent.
2. Check the number of pages on your website
As a website admin, you have an approximate idea of the number of indexed pages on your website. Google your website with the site search operator, and check the number of results. If the number of results exceeds your approximation significantly, it means that more pages of your website are being indexed on Google. If you didn’t create those pages, then they are a result of malware.

3. Check activity logs
An activity log is an essential admin tool for website management, especially if you want to know what each user is doing. In the case of malware, check the activity log for new users or those who have suddenly elevated privileges, like moving from Writer to Admin.
Ghost users can have weird usernames or email addresses, and these are the ones to look out for. If they change a bunch of posts and pages in a short period of time, then this is a good sign that the user accounts are fraudulent.

4. Look for strange trends in analytics data
Quite apart from the fact that hacks can cause Google to deindex your website altogether, there are some early warning signs that you can look for.
- Traffic sources and levels stay relatively the same, unless there is a change that prompts spikes, like a promotion. So spikes in traffic, especially from specific countries in short bursts of time can be indicative of something fishy.
- Engagement data, like conversion goals and bounce rates can also take a hit with hacks. Are people visiting your pages less? Why would that happen if SEO data and other factors remain the same? These are the kinds of questions you can ask of your analytics, as you would largely know what it should be.
5. Check for fake plugins
In your website’s /wp-content folder, you should see only plugins and themes that you have installed. Any weird ones with short, meaningless names, and perhaps ones that don’t follow naming conventions are the ones to scrutinize carefully.
Typically fake plugins will have a single file in the folder, or 2 at the very most.
6. Look for reported vulnerabilities in your plugins and themes
On your WordPress dashboard, look for plugins that have an ‘Update available’ tag. Next, Google to check if they have experienced any vulnerabilities recently. You can cross-reference the reported vulnerability with the type of hack it is susceptible to and figure out if your website is experiencing any of those telltale signs.

Some hacks are entirely invisible to admin, and there are others that are only visible to search engines. That is the nature of malware. It is difficult to pinpoint with any degree of accuracy without a proper scanner.
7. Check the .htaccess file
The .htaccess file is responsible for directing incoming requests to various parts of your website. For example, if your website is being accessed from a mobile device, the .htaccess loads up the mobile version of your website, instead of the desktop version.
If you are familiar with core WordPress files, check out the .htaccess file. Are the user agents loading up the correct files?
Malware like the SEO spam hack or the Japanese keyword hack will change the code of the googlebot user agent. Most commonly, it should load up the index.php file, but if it is hacked and a visitor clicks through from Google, an entirely different website will load instead of yours. Visiting your website directly, with the URL in the address bar, will load up the correct website, because the user agent detected is not googlebot.
8. Look for alerts from existing security plugins
Although this is not technically a diagnostic, we’re including previously installed security plugins in this list as well. If your security plugin scans your website regularly, it should alert you to any hacks. Depending on the security plugin you use, the alerts can be genuine or false positives. Our recommendation is to take every alert seriously because while false positives are unnecessarily alarming, on the off chance that the threat is genuine, much loss can result from ignoring a threat.
With MalCare, because of the way we have built our malware detection engine, the chances of a false positive is slim to none. That’s why website admin relies on our plugin to keep their websites safe.
There is a common misconception that installing several security plugins makes your website safer, presumably because whatever one plugin misses, the other one will catch. The problem with this premise is two-fold:firstly, that’s not actually the case. New and sophisticated malware will slip through most security plugins, except MalCare; and secondly, by adding multiple security plugins, you’re effectively weighing down your website so much, it will impact its performance dramatically.
How to clean your hacked WordPress site?
A hacked WordPress website is a scary prospect. We’ve spent a great deal of time in this article to figure out whether or not it is hacked. If you scanned with MalCare, you will have a definitive answer one way or another.
There are 3 options you have when dealing with a hacked WordPress site:
- Use a security plugin to clean the hack
- Hire a WordPress security expert
- Clean the hack manually
We will talk about each of these in turn.
A. [RECOMMENDED] Use a security plugin to clean your website
We recommend you use MalCare to clean your website of hacks. It is by far the best security plugin for WordPress websites, and uses an intelligent system to remove only malware, while keeping your website entirely intact.
To use MalCare for WordPress hack cleanup, all you need to do is:
- Install MalCare on your website
- Run the scan, and wait for the results
- Click auto-clean to surgically remove the malware from your website

The cleanup takes place in a matter of minutes, and your website is pristine once again.
If you used MalCare to scan your website when you were checking for malware, then all you need to do is upgrade and clean.
Why do we recommend MalCare?
- Removes only hacks from files and the database, leaving good code and data perfectly intact
- Detects vulnerabilities and backdoors that hackers leave behind and addresses those as well
- Comes with an integrated firewall to protect your website from brute force attacks
MalCare protects thousands of websites daily, and takes a proactive approach to website security. If you need further assistance with your website, our support team is available 24/7 to help users.
B. Hire a security expert to clean hacked WordPress site
If your WordPress website has been hacked for a while, your web host may have suspended your account and taken your website offline. Therefore, it isn’t possible to install a security plugin to clean the hack.
Don’t worry, in these cases, contact our emergency malware removal service to fix hacked WordPress site. A dedicated security expert will guide you through speaking to your web host to get IPs whitelisted to regain access, and therefore install the plugin for cleaning.
If your web host refuses to whitelist IPs because of their policies, then the expert will use SFTP to clean your website of malware in the shortest amount of time.
You can also opt to go with a WordPress security expert outside of MalCare. However, please be aware that security experts are expensive, and they do not guarantee against reinfection. Many security plugins that perform manual cleanups charge per cleanup, which is a cost that adds up very quickly with repeated infections.
C. Clean WordPress hacked infections manually
It is possible to remove malware manually from your website. In fact, in extreme cases, it is sometimes the only viable option. However we keep advising against it, and we’ve expanded a little on our reasons below.
If you do choose to clean up hacked WordPress website manually, then you should have a few prerequisites in order to be successful:
- You understand WordPress thoroughly. The file structure, how the core files work, how the database interacts with your website. You will also need to know everything about your website:plugins, themes, users, etc. The malware can be hidden in any file, including important ones, and if you merely delete the file, you can break your website.
- You need to be able to read code and understand code logic. For instance, removing a hacked file from the root folder is a good thing. But if your .htaccess file was loading that file on login, then your visitors will see a 404 page.
This is not an easy thing to know, and many scanners generate false positives because they cannot distinguish between custom code and bad code.
- Familiarity with cPanel tools, like File Manager and phpMyAdmin. Also, make sure you have SFTP access to your website. Your web host can help with getting that information.
1. Get access to your website
If your web host has suspended your account, or taken your website offline, you need to regain access to it. If you use SFTP, this is not an obstacle, but it is best to ask them to whitelist your IP so that you can view the website at the very least.
Additionally, the web host suspended your account after scanning your website and detecting malware. You can reach out to their support to ask for the list of infected files. Frontend scanners will also give you this information, although it may not be completely accurate and/or have false positives.
2. Take a backup of your website
We cannot stress this enough:please take a backup of your website before doing anything at all to it. A hacked site is much better than no site.
Firstly, things can go awry when people poke around in website code, and often do. That’s when backups save the day. You can restore the website, and start again.
Secondly, web hosts can delete your website altogether, if it is hacked. They have a vested interest in making sure there is no malware on their servers, and they will do whatever is necessary to ensure that is the case.
If a web host deletes your website, the chances of them having a backup are slim. Getting that backup from their support is even slimmer. We strongly advocate taking your own backups always.
We also recommend using a WordPress backup plugin for large files. We have seen restore fails abysmally with web host backups. When your website is hacked and you are cleaning it, you want to reduce complexity and chances of failure as much as possible.
3. Download clean installs of WordPress core, plugins and themes
Make a list of the versions that are on your website, and download clean installs of the core, plugins and themes from the WordPress repository. If you weren’t using the latest version of anything, make sure to download the version that was installed on your website. This is an important step, because you will be using the installs to compare files and code first.
Once you have downloaded and unzipped the installations, compare the files and folders with the ones on your website. To speed up the comparison process somewhat, use an online diffchecker to ferret out the differences in code.
Incidentally, this file matching is the primary mechanism that most scanners use. It is not a perfect mechanism, because you may have important custom code that will not show up in the clean installs. Therefore, now is not the time to delete. Take lots of notes, and mark out which files and folders are different from the originals.
This is also a good way to discover if your website has fake plugins installed. You will not find fake plugins on the repository, and they invariably do not follow plugin naming conventions and have very few files (sometimes just one) in the folder.
Note:Are you using nulled plugins or themes? Installing nulled software is like rolling out the red carpet for malware. When you pay for premium plugins, you are getting maintained software, the expectation of support in case something goes wrong, and the guarantee of safe code. Nulled software often comes packaged with backdoors or even malware.
A quick reminder to backup your website, if you chose to skip this step earlier. This is go-time. Cleaning malware out of your website is the hardest (and the most terrifying) step in this process.
4. Reinstall WordPress core
Use either File Manager in cPanel or SFTP to access your website files, and replace the following folders entirely:
- /wp-admin
- /wp-includes
You can do this without a problem, because none of your content or configurations are stored in these folders. As a matter of fact, there should not be anything in these folders that differs from the clean installations.
Next, check the following files for strange code:
- index.php
- wp-config.php
- wp-settings.php
- wp-load.php
- .htaccess
In a later section, we will talk about individual hacks and malware and how they appear in files and folders. Malware can manifest in many different ways, and there is no surefire way to identify them visually. You may come across advice online to look for odd-looking PHP scripts in these files, and get rid of those. However, this is very poor advice and users have flocked to our support team in the aftermath of breaking their websites. MalCare tests out each script to evaluate its behavior before determining if it is malicious or not.
Speaking of PHP files, the /wp-uploads shouldn’t have any at all. So you can delete any that you see there with impunity.
So we can’t actually predict what malicious code you are likely to see in any of these files. Please refer to a comprehensive list of WordPress files to understand what each does, their interconnectivity with each other, and if the files on your website behave differently. This is where an understanding of code logic will be immensely helpful.
If it is an entire file that’s bad, our advice is not to delete it right off the bat. Instead, rename the file extension from PHP to something else, like phptest, so that it cannot run anymore. If it is code in a legitimate file, then you can delete it, because you have backups if something breaks.
5. Clean plugin and theme folders
The /wp-content folder has all the plugin and theme files. Using the clean installs that you have downloaded, you can perform the same check as with the WordPress core installation and look for differences in the code.
We just want to point out that changes are not necessarily bad. Customizations will show up as changes in the code. If you have tweaked settings and configurations to get a plugin or theme to work just so on your website, expect to see at least minor changes. If you don’t have an issue wiping out customization entirely, then replace all the plugin and theme files with the fresh installs.
Generally, people are unwilling to write off any work they have put in, with good reason. So a lengthier method is to examine the code for differences instead. It is helpful to know what each script does and how it interacts with the rest of the website. Malware scripts can exist harmlessly in one file, until they are executed by another entirely innocuous-looking script in a completely different location. This tag team aspect of malware is one of the reasons it is so difficult to clean websites manually.
Another aspect of cleaning plugins and themes is that there can be a lot of them. Going through each one is a painstaking and time-consuming process. Our advice is to start in the most typical places to find malware.
In the files of the active theme, check:
- header.php
- footer.php
- functions.php
In the diagnostics section, we talked about researching if any of the plugins installed had a recently discovered vulnerability. We recommend starting with those files. Questions to ask here are:
- Have any been hacked recently
- Are any not updated
Did you find any fake plugins in the previous step? Those you can delete without a second thought. Although, don’t stop looking after that! The malware hunt isn’t over just yet.
Keep in mind that malware is supposed to look normal, and will mimic legitimate file names. We’ve come across some wolves in sheep’s clothing, where the stock WordPress themes like twentysixteen or twentytwelve have small typos that make them look virtually the same.
The clean installs will help with comparison and identification, but if you are unsure, contact the developers for support.
6. Clean malware from database
Extract the database from your backup, or if you haven’t taken one as yet, use phpMyAdmin to get a download of your database.
- Check the tables for any odd content or scripts in your existing pages and posts. You know what these are supposed to look like and do when they load on your website.
- Look for newly created pages and posts too. These will not show up in your wp-admin dashboard.
In some cases, like the redirect hack, the wp_options table will have an unfamiliar URL in the site_URL property. If the redirect malware is in the wp_posts table, it will be in every single post.
Revert modified settings to what they should be, and remove malicious content carefully.
Again, depending on the size of your website, this can be a gargantuan task. The first hurdle is to identify the malware, and where it is. If it is the same malware script on each post and page, then you’re in luck. You can use SQL to extract the content from every file. However, be warned that, while removing a single lot of malware is great, you cannot be sure that’s the only hack on your website.
If you have an e-commerce website, with critical user and order information, double- and triple-check you are indeed getting rid of malware only.
7. Check your root for suspicious files
When going through the files of your website, have a look at the root folder too. It can also have malware files stored there. All PHP files are not bad, and some plugins add scripts to the root to perform certain tasks. For instance, BlogVault adds its Emergency Connector script to the root of a website, so that the plugin can restore a backup even if the site is inaccessible. Other security plugins will flag it as malware, even those it definitely isn’t.
8. Remove all backdoors
Malware often leaves behind exploits in websites known as backdoors, just in case they are discovered and removed. Backdoors enable hackers to reinfect websites almost immediately, therefore wiping out all the cleaning effort.
Just like malware, backdoors can be anywhere. Some code to look for is:
- eval
- base64_decode
- gzinflate
- preg_replace
- str_rot13
These are functions that allow external access, which is not inherently a bad thing. They have legitimate use cases, and are often altered subtly to act as backdoors. Exercise caution when deleting these without analysis.
9. Reupload your cleaned files
The worst is over, now that you have cleaned out the malware from your website. Now it is a question of rebuilding your website. First, delete the existing files and database, and then upload the cleaned versions in their place.
Use File Manager and phpMyAdmin on cPanel to do this for files and the database respectively. By now, you are a pro at handling these features. If you need more help, you can refer to our article on restoring a manual backup. The process is the same.
Don’t be discouraged if large restores don’t work. cPanel struggles to handle data above a certain limit. You can use SFTP to do this step as well.
10. Clear the cache
After putting your site together again, and checking it a few times to see if everything works as expected, clear the cache. The cache stores earlier versions of your website, in order to reduce loading time for visitors. So that your website behaves as expected after the clean-up, empty out the cache.
11. Verify each of the plugins and themes
Now that you have reinstalled your website, with cleaned versions of this software, check the functionality of each. Do they work as you expected?
If yes, that’s great. If not, go back to the old plugin folders and see what didn’t make it over to the cleaned website. Chances are, some of that code is responsible for the missing functionality. You can then replicate the code to your website again, being very cautious that those bits aren’t malware-ridden.
We recommend you do this one plugin and theme at a time. You can rename the plugin folders temporarily, thereby effectively deactivating them. The same method works for theme folders.
12. Repeat this process subdomains and nested WordPress installations
This may not apply to you, but we’ve seen several websites with second WordPress installations on their main site. This could be the result of several things, like a site design, a subdomain, or even a forgotten staging site.
If there was malware on your primary WordPress site, then it could and will have contaminated the nested installation. The reverse is also true. If your nested installation has malware, it will reinfect the website you just cleaned.
Typically, we ask users to remove any unused WordPress installations altogether. They are an unnecessary hazard.
13. Use a security scanner to confirm
You’re almost at the finish line! This was a rough ride, and you should take a moment to appreciate the feat you pulled off. Even WordPress experts aren’t always comfortable with a WordPress hack cleanup manually, preferring to use tools instead.
All that’s now left is to confirm that the malware has really gone from your website. Use MalCare’s free scanner to get that confirmation, and you are good to go!
Why you should avoid manually cleaning a hacked WordPress site?
We strongly advise against manual cleaning, even though we have included the steps above. If you liken a hack to an illness, you would rather a qualified medical professional perform life-saving surgery, wouldn’t you? Imagine trying to remove your appendix yourself, and you get where we are going with this analogy.
Hacks, like invasive infections, get progressively worse with time. If malware is destroying your website data, for instance, acting fast could save you a great deal of time and resources. Not to mention, save your website too.
As malware replicates itself, it spreads into different files and folders, creates ghost admin users to regain entry if it is detected, and overall wreaks havoc.
On top of this, recovery becomes significantly harder. We’ve had users come to us with half-destroyed websites that they’ve tried to clean themselves, failed, and now are in desperate straits, trying to save whatever is left. We can do our best, but we can’t magic back their lost data for them—a situation that could have been avoided with some timely action.
The only reason we are reiterating this so many times is that we genuinely care about our users, and feel terrible every time we have to tell them that their data cannot be retrieved.
To recap, here are the things that can go wrong with manual WordPress hack removal:
- Malware can spread into unexpected places, and is difficult to find. If you clean only some of it, the rest will soon reinfect your website again.
- Removing just the malware is not good enough if the vulnerability and/or backdoor isn’t found and resolved
- You have to know what each file does and how it interacts with others, otherwise, you could inadvertently break your website
- Large sites (like e-commerce stores) will take ages to go through, file by file. It’s like looking for a needle in a haystack.
- And last by not least, hacks cause increasingly more damage as time wears on
There are so many things that can go horribly wrong with manual cleanups. Trust us, we have seen our fair share. If your wordpress site is compromised, the best course of action to return your site to good health is to install a security plugin.
Why you shouldn’t repair your website using a backup?
In spite of being huge advocates of backups, we do not recommend reverting your website to a previous version. There are several reasons for this:
- You will lose all the changes you made in between
- The backup shouldn’t have the malware either, and unless you have a precise idea of when your website had malware, this is hard to ascertain
- The backup will have the vulnerabilities that led to the malware infection in the first place
The only time you should consider using a backup as a starting point is if the malware has destroyed your website and data beyond retrieval. We genuinely hope that it doesn’t ever reach that stage, and installing a good security plugin will save you from these issues in the future.
How to revert damage after removing hacks
Once your website is free of malware, you can now focus on reverting the damage caused by the hacks in the first place. There are two main stakeholders (apart from your visitors and you) with respect to your website:the web host and Google.
Regaining access to a website
Contact your web host once you are done with the cleaning, and ask them to rescan your website. You can also detail the steps you have taken in order to resolve the issue. Invariably, this will result in your access being restored and your site being back online.
Getting your site removed from Google’s blacklist
If your website landed up on Google’s blacklist, then you need to request a review. You can do that by going into your Google Search Console and clicking on Security Issues. There, you should see an alert for harmful content, detailing which files contain them.
At the very bottom of this alert, you will find a button to request a review. You have to undertake that you have fixed the issues, and provide a detailed explanation of all the steps you took for each issue listed.
Once the request is submitted, you should hear the outcome of the request in a few days.
Brand damage control
This step is purely optional, and it is just advice. As we will talk about later, hacks almost always damage reputation. If you can, publicly acknowledge what happened, what steps you took to fix it, and how you plan to prevent it in the future.
Honesty goes a long way in rebuilding relationships, and there have been instances where well-handled hacks have led to increased brand value.
How to keep your WordPress site from being hacked?
One of the worst parts about malware is that it keeps coming back, either through backdoors or through exploiting the same vulnerabilities as before.
We share this security checklist with our customers to help them prevent WordPress sites from being hacked in the future.
- Install a security plugin: We cannot sufficiently emphasise the benefits of a good security plugin like MalCare, which can scan, clean, and prevent hacks. In addition to being able to quickly diagnose and clean hacks, MalCare protects your website from a lot of Internet nastiness, like bots, with an advanced firewall. The best part about MalCare is that, unlike other security plugins, it will not use up your server resources, so your site will hum along optimally and still be protected.
- Change all user and database passwords: After vulnerabilities, poor passwords and the resulting compromised user accounts are easily the top reason for hacked websites.
- Reset user accounts: Get rid of any user accounts that shouldn’t be there. Review the privileges of those that should be there, only granting the minimal privileges required for the individual user.
- Change salts + security keys: WordPress attaches long strings of random characters, known as salts and security keys, to login data in cookies. These are used to authenticate users, and to make sure they are logged in safely. To change these, WordPress has a generator, after which the updated strings can be put into the wp-config.php file.
- Choose your plugins and themes wisely: We highly recommend sticking to plugins and themes from reputed developers only. Not only will the developers provide support when required, but will maintain the plugin or theme code with constant updates. Updates are critical to patch vulnerabilities, and are your first line of defence against hacks.
If you feel that nulled themes and plugins will save you money, you will end up losing whatever you save many times over when the inevitable hack occurs. Nulled themes and plugins are not only unethical, but downright dangerous.
- Install SSL: SSL protects the communication to and from your website. SSL uses encryption to make sure it cannot be intercepted and read by anyone else. Google has been advocating for SSL implementation on websites for years now, and actively penalises website SEO if the website doesn’t have SSL.
- Harden WordPress: There are measures to toughen up security, commonly known as WordPress hardening. We would caution you to be mindful of following the immense advice available online. Some of it is downright bad and will impact your website and visitors’ experience. Follow this guide to harden your website responsibly.
- Update everything: All updates, whether WordPress, plugin, or theme, are necessary and should be done as soon as possible. Updates usually address issues in the code, like security vulnerabilities. It is especially critical because when security researchers discover vulnerabilities, they disclose them to the developer who then releases a patch for it. The researcher then discloses the vulnerability publicly, and that’s when mayhem erupts. Hackers will try their luck with any websites that don’t have the update installed.
The resistance to WordPress updates is understandable, because it can disrupt operations, especially if something breaks. The safest way to implement updates is to use a staging site first, and then merge changes to live.
- Implement an activity log: In order to keep a close eye on changes made to your website, an activity log is immensely useful. Apart from monitoring regular changes, unexpected changes like new users can signal that someone has unauthorized access. It will help you catch hacks early.
- Use SFTP instead of FTP: Similar to SSL, SFTP is a secure way to use FTP to access your website backend on the server. Most admin avoid using FTP at all, because it tends to be slow and painstaking to work with. However, in case you cannot log into your website, FTP becomes necessary.
- Remove secondary WordPress installations if not in use: We’ve seen this several times. Malware reappears on freshly cleaned websites, because there is a second website on the same cPanel with malware. It works both ways in fact. If either of the sites has malware, it is only a matter of time before the other one is infected.
There are various reasons that you would have a second website installed on cPanel, and all of them are legitimate:site redesign, staging site, or even a subdomain. However, several times users forget about the second website, even to update or monitor it. It then gets hacked because of vulnerabilities, and the malware works its way into the main website.
- Choose a good host: This is a somewhat subjective point, but it pays to do research to pick a good host. The general rule is to pick an established brand name and check how they have handled issues in the past. You want to have a web host that has responsive support, invests in their infrastructure, and has security certifications.
- Invest in backups: We’ve said this a few times already in this article, but backups are non-negotiable. Backups are invaluable when all else fails, and our customers have been able to retrieve 100% of their website even after really bad hacks solely because of backups.
- Have a security plan in place/things to do regularly: Last, but certainly not least, have a plan in place to run through diagnostics regularly. Also, there are a few things that should be done to a cadence:review users, require password changes, monitor activity logs, update regularly, check for vulnerability news, and so on. Often, these measures will help avert major security-related disasters early on.
How did your WordPress website get hacked?
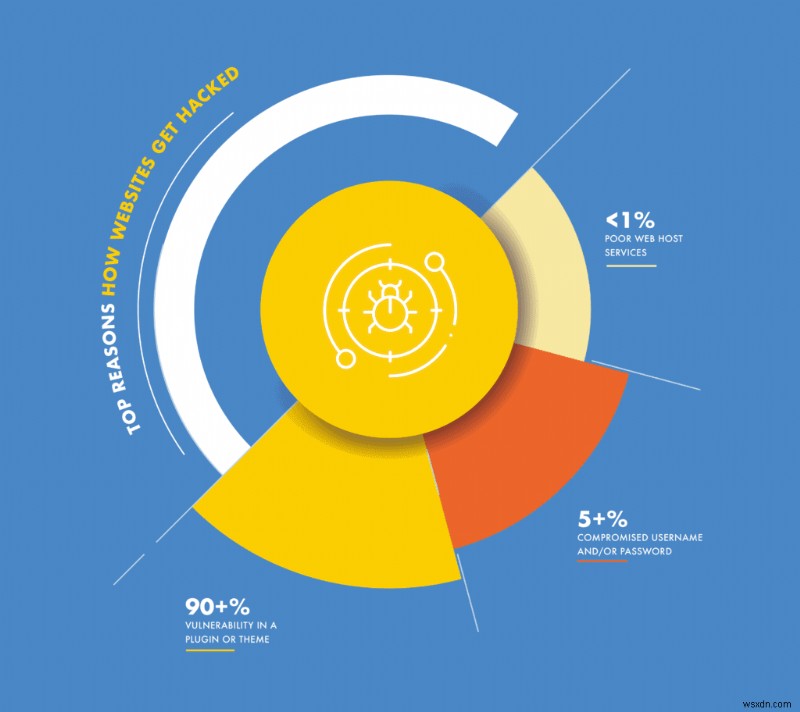
We like to think that everything we use is 100% secure, but that’s unfortunately not true. It isn’t true of our homes, and certainly not the case with our websites. No software is completely bullet-proof, and every part of the website is essentially software:right from WordPress itself, to the plugins and themes.
Vulnerabilities in plugins and themes
When code is written, developers can make oversights or mistakes. These mistakes are called vulnerabilities. Vulnerabilities are the single biggest reason why websites get hacked.
Of course, mistakes aren’t made deliberately. Vulnerabilities often just boil down to a developer writing code to accomplish one task, without realizing that a hacker can use the same code in an unintended way to gain unauthorized access to the website.
A good example of this concerns the /wp-uploads folder. In the cleaning section, we mentioned that the /wp-uploads folder should never have PHP scripts. The reason being that the contents of the folder are publicly accessible via the URL and the name of the file.
Therefore, PHP scripts in the uploads folder would also be accessible, and as a result, remotely executable. Therefore the folder should have a check to ensure that the uploads are not PHP files. If someone does try to upload a script, it should be rejected.
To see a list of WordPress vulnerabilities, check out WPScan.
This example also brings up an interesting point. One could argue that the uploads folder should not be publicly accessible, so PHP scripts would not be accessible either. However, this interferes with the functionality of the folder and is not a good fix.
Similarly, we see a ton of poor security advice on the internet, which fixes a vulnerability without taking functionality into consideration.
Undetected backdoors
A backdoor is very much what it sounds like:a way to gain unauthorized access without being detected. Even though backdoors are technically malware—code that has malicious intent—they are not actively damaging. They allow hackers to insert malware into the website.
This distinction is important because it is the primary reason WordPress websites get hacked again after cleanups. Cleanups are effective at getting rid of malware, but not addressing the entry point of the malware.
Security plugins will often flag backdoors by looking for certain functions. But there are 2 problems with this method:firstly, hackers have found ways to mask the functions effectively; and secondly, the functions are not always bad. They have legitimate uses too.
Poor user management policies
There is always an element of human error with hacks, and it mostly comes in the form of the misuse of admin accounts. As a website admin, there are a few things you should always keep top of mind when considering the security of your website.
Weak passwords
Yes, we know passwords are hard to remember. Especially ones that are a mix of characters, and long enough to be considered ‘safe’. However, easier-to-remember passwords are a weak link to your website security. Even a security plugin cannot protect your website if a password has been compromised.
Think of your website like your home, where you’ve installed a state-of-the-art security system, like MalCare. If a thief were to learn your unique passcode to gain entry to your home, the security system wouldn’t be able to do anything.
Strong passwords are critically important for all accounts, but even more so for admin accounts, which brings us to our next point.
Unnecessary user privileges
Users should only ever have enough privileges to accomplish what they need to on a website. A blog writer doesn’t need admin privileges to publish a post, for instance. It is very important to make sure to review these privileges regularly.
Additionally, if a website admin is vigilant about user account levels, an activity log is a great tool to have as well. The activity log lists all the actions performed by users on a website and can be a great early indicator of a compromised user account. If a user who usually writes posts suddenly installs a plugin out of the blue, it is a warning sign.
Old accounts are still active
In addition to reviewing accounts, also remove unused user accounts regularly. If a user is no longer active on your website, there is no reason why their account should be. The reason is the same as before:user accounts can be compromised. Hackers can get hold of credentials and escalate their privileges to admin accounts.
Unsecured communication
Apart from the actual website, communication to and from the website also needs to be secured. If communication is intercepted and is not secured, it can be read easily. So it should be encrypted. This can be easily accomplished by adding SSL to your website.
In fact, SSL is becoming the de facto standard of the internet. Google actively rewards the use of SSL, by punishing websites without it in the SERPs. Some websites show up in the search results as ‘Site not secure’, as part of their Safe Browsing initiative.
On similar lines, it is always better to use SFTP instead of FTP, whenever possible.
Web host issues
In our experience, web hosts are rarely responsible for hacks. Most hosts implement loads of security measures to make sure that the websites they host are secure.
For instance, people often think that their websites have got malware because they are on shared hosting plans. This is a misconception most of the time, because hosts implement barriers between sites. The real cause of cross-site infections is when there are multiple WordPress installations on a single cPanel instance.
Is WordPress more prone to hacks than other CMS?
Yes and No.
The immense popularity of WordPress means that it attracts a lot more hackers to it. Very simply, there is a larger payoff for hackers if they are able to discover and exploit a vulnerability in the ecosystem.
Additionally, WordPress-related vulnerabilities get a lot more attention, again because of its popularity. Similar instances with, say Joomla, would not merit as much discussion.
In actual fact, WordPress has solved many of the problems that still exist with other CMS. It also has a terrific community and ecosystem as well. Help and support is easily available, even for niche and specific issues that a website admin may face.
Understanding WordPress hacks
If you have a security plugin like MalCare installed, you don’t need to worry about hacks. We constantly upgrade the plugin to counteract new attacks, in order to protect websites better. However, it is interesting to understand how hacks work, so that you can see just how critical a good security plugin is.
We’ve broken this section up into 2 parts:
- Hack mechanisms: How malware is inserted into the websites by either exploiting vulnerabilities or attacking the website.
- Types of malware: How the malware manifests itself on your website. There are a few ways that malware shows up on your website, but ultimately the hacker’s goal is to get unauthorised access to perform otherwise prohibited activities. We’ve expanded on why WordPress sites get hacked in a later section.
Hack mechanisms
Previously in the article, we have talked about how websites get hacked. Either through vulnerabilities or backdoors, or sometimes poor passwords. These are flaws within the security of the website and are akin to weak points of a structure.
Hack mechanisms are the weapons used to attack those weak points. Their goal is to insert malware into the website. They are bots or programs that target weak points in specific ways to achieve their goal. There are several hack mechanisms, especially since hackers are getting smarter every day about circumventing the security systems of websites.
- SQL injection: SQL is a programming language used to interact with database systems, in order to write, read or manipulate data. Websites interact with the database all the time, to save form data for instance, or to authenticate users. An SQL injection attack uses SQL to insert php scripts into the database.
The injection is only possible if the form is not adequately protected from incorrect inputs. The hacker can use operators and programming logic to circumvent the functionality of a form, unless checks are put in place.
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): Cross-site scripting(XSS) is also the injection of code, like with SQL injection, but into the browser. The next user to access the website or otherwise interact with the page in question becomes the target of this attack.
Again, form fields are duped by hackers into accepting code like JavaScript and executing those scripts without validation.
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS): In a DDoS attack, hackers flood a website or system with so much malicious traffic that legitimate users cannot access it. The attack works because resources are limited or metered.
For instance, a website using server resources will be on a plan for processing power and request handling. If the website is bombarded with 100x or even 1000x requests compared to what it normally receives, the server will not be unable to handle those requests and visitors will see an error.
- Brute force attacks: This type of attack usually targets login pages, trying out combinations of usernames and passwords in order to gain access to the website. The hack mechanism is a bot, and will try out passwords, using words from a dictionary. A brute force attack also consumes server resources, and so will often end up keeping out genuine users and visitors.
On many WordPress support threads, you will see advice to hide the login page to protect from this attack. This is an unwise thing to do, because the URL can be forgotten, it is tricky to distribute this URL to multiple users for login, and many more problems. It is best to have bot protection in place that keeps out this bad bot traffic.
Types of malware
The malware types we have listed appear to mirror symptoms closely. That’s because most malware has been named for the symptoms that each display. If you were to drill down into the malware, they aren’t all that different in construction or purpose.
All malware is out to use your website in some way or the other:use up its resources, steal data, piggyback on your SEO rankings, etc. The most commonly seen malware are:
- Pharma hack: Your website will have new pages or posts filled with keywords or links to sell pharmaceutical products, often grey market or illegal. These products are difficult to rank for on Google because of legality issues, and hence to get more traffic and sales, hackers insert these pages into unsuspecting websites.
To detect a pharma hack on your website, you can try Googling pharma keywords like ‘viagra’ or ‘CBD’ with the search operator site:. It will list out all the pages on your website with that keyword.
- Japanese keyword hack: The Japanese keyword hack is a variation of the pharma hack, and indeed of the next malware on this list, the SEO Spam hack. The only difference is that instead of pharmaceutical products, the malware will display Japanese content; often, unsavoury adult content.
It is a little harder to check for this hack, unless you are familiar with Japanese and can look for keywords.
- SEO spam hack: The SEO spam hack, as said before, is a variation on the first two. The content differs. Here, the spam content can include online gambling and casinos, or shady products. This is effectively a catchall term for all hacks that insert extra pages into your website, but don’t fall into one of the special categories.
- Redirects: Malicious redirects take place when a visitor to your website is taken to an entirely different website, usually a spammy one. There are a few variations of the redirect hack, depending on where it appears.
The most egregious aspect of the redirect hack is that website admin cannot log into their websites. Therefore, they cannot control the damage or even fix their website without expert help.
Examples of hack scripts, we’ve found in websites:



It is difficult to protect against all the hack mechanisms, which is why installing a security plugin is very critical. MalCare’s sophisticated algorithm combats malware effectively, in addition to protecting websites against hack mechanisms.
What are the consequences of a hacked WordPress site?
The impact of a hacked WordPress website can be wide-ranging in bad consequences. The importance of web security cannot be sufficiently overestimated because of this reason. Website admins without exposure to cybersecurity may read about the occasional hack, but the full potential impact is not always evident.
Therefore, it is critical to understand the impact in its entirety. The poor consequences are not confined to individual websites or their owners and administrators but have far-reaching implications.
Immediate impact on your website
If your WordPress website is hacked, there are chances you won’t even realise it for a while. Rest assured, whether or not you can see a hack, the damage is unfolding and getting worse as time wears on.
Let’s say one of the ways the hack manifests is through malvertising; a very common sign with spammy ads or pages that redirect your website visitors to another website (usually a pharma site or one peddling illegal stuff). This has several implications:
- Google blacklist: Google is hyper-vigilant about hacked websites, because they do not want to send their users (search engine users) to dangerous websites. With malware, your website is now dangerous. So they will put up a massive, scary red notice advising visitors to stay far away from your website.
Additionally, other search engines and browsers use this same blacklist to protect their own users. So even if your site doesn’t get flagged with the red screen, most browsers will warn your visitors away with messages.
- SEO rankings will tank: As a result of fewer visitors and Google’s policy of protecting people, your website will stop showing up in results. Google calls this “hiding sites silently”. Not only are you going to lose ground you may have gained with an SEO strategy, but you will also lose visitors and discoverability.
- Loss of trust and visitors: Most people will see spam content as a sign of a hack and know that your website is unsafe. If you are fortunate, someone will point it out. If not, your traffic numbers will decline.
- Web host issues :Web hosts will quickly suspend websites that are hacked. If your website is hacked, your web host will face a lot of the heat, and will take hacked websites offline as soon as they are discovered to be hacked.
A web host risks their IPs getting blacklisted with a hacked site. If your website is used for phishing attacks, and firewalls identify your website as the source, that means your IP address can be blacklisted, which will cause the host several issues.
Also, a hacked website will often consume lots of server resources, and if your website is on shared hosting, that will adversely affect the performance of other websites, which are other customers of the web host. The problem becomes worse if there are bots attacking your website. Bots pummel your website with thousands and thousands of requests that consume tons of resources.
- Unwitting pawn: Your website becomes a host for malware; part of a botnet that goes on to attack more websites.
Business impact
The impact of the previous section applies to all websites, large and small. The consequences are worse if your website is central to your business. Because then we are talking straight up the monetary loss.
- Loss of revenue: Downtime, poor SEO rankings, visitor numbers reducing are all contributing factors to loss in revenue. If people can’t or won’t visit your website, you aren’t going to get business that way.
- Degraded branding: Trust is a huge commodity in online marketing, and hacks erode that trust. You may have had a competitive advantage in some cases. That too will be affected. Also, data breaches leave a stain on reputation. Some businesses handle the aftermath well, but the seed of doubt may be planted forever. Since things last forever on the Internet, a quick, intentional Google search will bring up hacks. It will become a point of consideration for any potential customer.
- Server resources: We mentioned this in the previous section, but it bears mention from a monetary angle as well. Web hosts charge for excessive resource consumption. If your hacked website goes undetected for a while, you could also be paying for this fraudulent usage. Plus, if you are subject to bot attacks, the rapid depletion of (finite and allocated) server resources means that legitimate users will not be able to access your website.
- Investment: You’ve spent time, money, and manpower to build this website. If you lose the website, you’ve lost that investment.
- Legal issues: Data breaches of private information can cause you legal issues because of stringent data protection regulations. It is very important that websites that collect personal data from visitors treat that data with the utmost care. If it is compromised in any way, those people have grounds for legal action.
- Cleaning cost: Hack removal is an expensive proposition, especially if you hire experts who actually know what they are doing.
Apart from that, we often encounter website admin who try cleaning malware out by themselves, and cause their website to break. Then, in panic, they seek out expert help. Again, data retrieval is an expensive undertaking.
Dangerous for people
Social engineering attacks, like phishing, have compounded impact. They are bad for the website and website admin being attacked, but also have terrible consequences for their users and visitors.
Credentials can be used to hack into other websites. Hackers can use aggregated information from websites to create personal profiles that can be used to hack into bank accounts and other restricted areas. People also tend to use the same passwords in multiple places, making them especially vulnerable in these situations.
While all data theft is bad, it takes a tragic turn with the theft and release of information of vulnerable people, like those in witness protection programs or on the run from abusers. This information sells on the dark web, a particularly ugly place.
Why do WordPress websites get hacked?
All websites have value, whether large or small, business or personal. Many website owners of small blogs often have a false sense of security because they feel their website is “too small” to be hacked.
This is not true at all. While bigger websites will have a bigger payoff for hackers in terms of data theft for instance, smaller sites have value of their own. They can be used as a part of a botnet, for example. Or a site may have a small, dedicated following, which can be tapped for phishing scams via their email addresses.
Bởi vì mọi người có xu hướng sử dụng cùng một mật khẩu cho các tài khoản khác nhau, về mặt lý thuyết có thể xâm nhập vào một trang web hoặc hệ thống khác bằng cách sử dụng thông tin này. The small website played a small but crucial role in this chain of events.
Finally, hacking is always worth the effort. Hacks are rarely carried out manually. Malware, bots specifically, are designed to automate the hacking process. So there is minimal “effort” on the hacker’s front. Thus the gains of hacking your site are disproportionately stacked on the side of hackers.
Conclusion
In order to protect your website, it is important to be well-informed about WordPress security and hacks. In this article, we have attempted to explain WordPress hacks, motivations, impact, and much more, so you can make an informed decision about your website’s security.
We recommend MalCare to fix hacked WordPress website because it is a complete security solution, and is only getting better with time. We protect 1000s of websites daily, with our advanced firewall, scanning and cleaning algorithm, and much more. MalCare has found malware that most other scanners miss, and has saved our customers untold amounts in revenue.
We would love to hear from you. Reach out to us via email for any questions, and we’re happy to help.
FAQs
How do WordPress sites get hacked?
Primarily, WordPress websites get hacked or keep getting hacked because of vulnerabilities in the core WordPress files, plugins, or themes. Hackers exploit these vulnerabilities to insert malware into the website. The second biggest reason that websites get hacked is because of poor or insecure passwords.
My WordPress site has been hacked, what to do?
If your WordPress site is seriously compromised, there are steps you can take to fix the hack:
- Scan your website for malware using MalCare
- Take a backup of your hacked WordPress site before cleanup
- Use a security plugin to clean up hacked WordPress site
- Install a web application firewall
- Change all user passwords
