Con đường Euler là một con đường; bằng cách đó chúng tôi có thể ghé thăm mọi cạnh chính xác một lần. Chúng ta có thể sử dụng các đỉnh giống nhau cho nhiều lần. Trong trường hợp này, một biểu đồ chứa Mạch Euler cũng được xem xét, vì nó cũng có đường dẫn Euler.
Để kiểm tra xem một biểu đồ có hướng có đường dẫn Euler hay không, chúng ta phải kiểm tra các điều kiện này -
- Phải có một đỉnh duy nhất a n ở đâu (in-Deg + 1 =out_degree)
- Phải có một đỉnh duy nhất b n ở đâu (in-Degree =out_degree + 1)
- Còn lại tất cả các đỉnh có (in-Deg =out_degree) nếu bất kỳ trường hợp nào trong số này không thành công thì biểu đồ không có đường dẫn Euler.
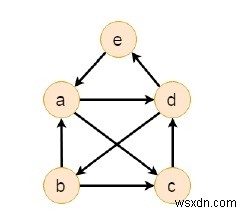
Đỉnh b có (trong bậc 1, ngoài bậc 2), đỉnh c có (trong bậc 2, ngoài bậc 1). Và đối với phần còn lại của các đỉnh a, d có (trong bậc 2, bậc 2), e có (trong bậc 1, ngoài bậc 1).
Đầu vào
Ma trận kề của biểu đồ.
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Đầu ra
Đã tìm thấy đường dẫn Euler.
Thuật toán
traverse (u, đã thăm)
Đầu vào Nút bắt đầu u và nút đã truy cập để đánh dấu nút nào được truy cập.
Đầu ra Đi ngang tất cả các đỉnh được kết nối.
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
isConnected (đồ thị)
Đầu vào:Biểu đồ.
Đầu ra:Đúng nếu biểu đồ được kết nối.
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
hasEulerPath (Đồ thị)
Nhập vào Đồ thị đã cho.
Đầu ra True khi tìm thấy một mạch Euler.
Begin an := 0 bn := 0 if isConnected() is false, then return false define list for inward and outward edge count for each node for all vertex i in the graph, do sum := 0 for all vertex j which are connected with i, do inward edges for vertex i increased increase sum done number of outward of vertex i is sum done if inward list and outward list are same, then return true for all vertex i in the vertex set V, do if inward[i] ≠ outward[i], then if inward[i] + 1 = outward[i], then an := an + 1 else if inward[i] = outward[i] + 1, then bn := bn + 1 done if an and bn both are 1, then return true otherwise return false End
Mã mẫu
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool hasEulerPath() {
int an = 0, bn = 0;
if(isConnected() == false){ //when graph is not connected
return false;
}
vector<int> inward(NODE, 0), outward(NODE, 0);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j]) {
inward[j]++; //increase inward edge for destination vertex
sum++; //how many outward edge
}
}
outward[i] = sum;
}
//check the condition for Euler paths
if(inward == outward) //when number inward edges and outward edges for each node is same
return true; //Euler Circuit, it has Euler path
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(inward[i] != outward[i]) {
if((inward[i] + 1 == outward[i])) {
an++;
} else if((inward[i] == outward[i] + 1)) {
bn++;
}
}
}
if(an == 1 && bn == 1) { //if there is only an, and bn, then this has euler path
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
if(hasEulerPath())
cout << "Euler Path Found.";
else
cout << "There is no Euler Circuit.";
} Đầu ra
Euler Path Found.
