Để biết về Euler Circuit, chúng ta có ý tưởng về Euler Path. Con đường Euler là một con đường; bằng cách đó chúng tôi có thể truy cập vào mỗi nút chính xác một lần. Chúng ta có thể sử dụng các cạnh giống nhau cho nhiều lần. Euler Circuit là một loại đường dẫn Euler đặc biệt. Khi đỉnh bắt đầu của đường Euler cũng được nối với đỉnh kết thúc của đường dẫn đó.
Để phát hiện mạch, chúng ta phải tuân theo các điều kiện sau:
- Biểu đồ phải được kết nối với nhau.
- Bây giờ, khi không có đỉnh nào của đồ thị vô hướng có bậc lẻ, thì đó là Mạch Euler.
Đầu vào
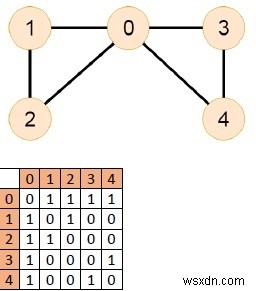
Đầu ra
Biểu đồ có mạch Euler.
Thuật toán
traverse (u, đã thăm)
Đầu vào Nút bắt đầu u và nút đã truy cập để đánh dấu nút nào được truy cập.
Đầu ra Đi ngang tất cả các đỉnh được kết nối.
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
isConnected (đồ thị)
Đầu vào:Biểu đồ.
Đầu ra:Đúng nếu biểu đồ được kết nối.
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
hasEulerianCircuit (Đồ thị)
Nhập vào Đồ thị đã cho.
Đầu ra Trả về 0, khi không có Mạch Eulerian và trả về 1 khi có mạch Euler ..
Begin if isConnected() is false, then return false define list of degree for each node oddDegree := 0 for all vertex i in the graph, do for all vertex j which are connected with i, do increase degree done if degree of vertex i is odd, then increase oddDegree done if oddDegree is 0, then return 1 else return 0 End
Mã mẫu
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //No Euler circuit, but euler path is present
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0}}; //uncomment to check Euler Circuit as well as path
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //Uncomment to check Non Eulerian Graph
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v]) traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int hasEulerianCircuit() {
if(isConnected() == false) //when graph is not connected
return 0;
vector<int> degree(NODE, 0);
int oddDegree = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j])
degree[i]++; //increase degree, when connected edge found
}
if(degree[i] % 2 != 0) //when degree of vertices are odd
oddDegree++; //count odd degree vertices
}
if(oddDegree == 0) { //when oddDegree is 0, it is Euler circuit
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
if(hasEulerianCircuit()) {
cout << "The graph has Eulerian Circuit." << endl;
} else {
cout << "The graph has No Eulerian Circuit." << endl;
}
} Đầu ra
The graph has Eulerian Circuit.
