Với cây nhị phân, hàm sẽ tạo ra các giá trị nhị phân của các khóa được lưu trữ trong các nút và sau đó trả về số lượng các bit đã đặt (1) trong tương đương nhị phân đó.
Ví dụ
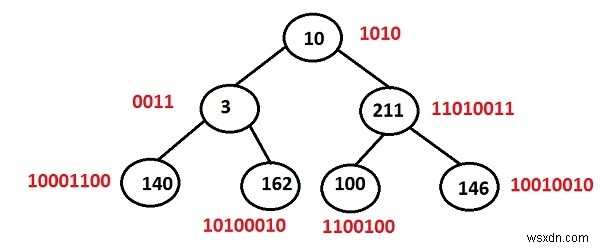
Cây nhị phân có các khóa là:10 3 211 140 162 100 và 146
| Phím | Tương đương nhị phân | Đặt bit (đầu ra) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1010 | 2 |
| 3 | 0011 | 2 |
| 211 | 11010011 | 5 |
| 140 | 10001100 | 3 |
| 162 | 10100010 | 3 |
| 100 | 1100100 | 3 |
| 146 | 10010010 | 3 |
Ở đây chúng tôi đang sử dụng hàm __builtin_popcount
Nguyên mẫu hàm như sau -
int __builtin_popcount(unsigned int)
Nó trả về số lượng các bit đã đặt trong một số nguyên, tức là số các bit trong biểu diễn nhị phân của số nguyên.
Thuật toán
START Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct Node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node->data = data node->left = node->right = NULL; return (node) Step 3 -> Create function for generating bits of a node data void bits(Node* root) IF root = NULL return print __builtin_popcount(root->data) bits(root->left) bits(root->right) step 4 -> In main() create tree using Node* root = newnode(10) root->left = newnode(3) call bits(root) STOP
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data) {
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
//function for finding out the node
void bits(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
//__builtin_popcount counts the number of set bit of a current node
cout << "bits in node " << root->data << " = " <<__builtin_popcount(root->data)<< "\n";
bits(root->left);
bits(root->right);
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(3);
root->left->left = newnode(140);
root->left->right = newnode(162);
root->right = newnode(211);
root->right->left = newnode(100);
root->right->right = newnode(146);
bits(root);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau
bits in node 10 = 2 bits in node 3 = 2 bits in node 140 = 3 bits in node 162 = 3 bits in node 211 = 5 bits in node 100 = 3 bits in node 146 = 3
