Với cây nhị phân, chương trình phải tìm ra đường đi ngắn nhất từ gốc đến lá trong số nhiều đường đã cho.
Vì chúng ta đi ngang cây từ trái sang phải, nên nếu có nhiều đường đi ngắn nhất từ gốc đến lá hơn chương trình sẽ in đường đi đầu tiên là đường ngắn nhất ở phía bên trái của cây.
Chúng ta có thể sử dụng một hàng đợi sẽ đi qua mỗi cấp bằng cách sử dụng truyền theo Thứ tự Cấp và đường dẫn có số cấp ít nhất sẽ được in vì nó sẽ là đường ngắn nhất từ gốc đến lá
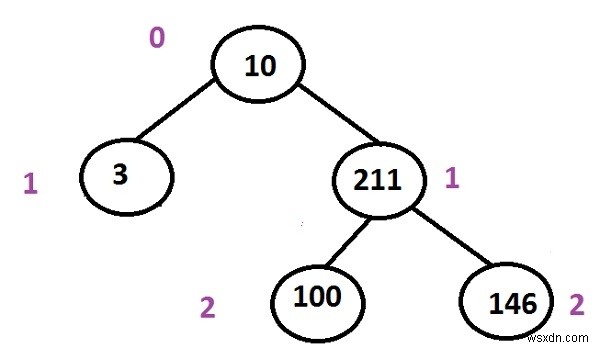
Trong cây trên, nhiều con đường từ gốc đến lá là
10 -> 3 (this one is the shortest path amongst all) 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
Ví dụ
Input : 10 3 211 100 146 Output : 10 3
Thuật toán
Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node *temp = new node temp->data = data temp->left = temp->right= NULL return temp Step 3 -> create function for calculating path void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) IF prnt[data] = data Return End path(prnt[data], prnt) print prnt[data] step 4 -> function for finding out the left path void left(Node* root) create STL queue<Node*> que que.push(root) int leaf = -1 Node* temp = NULL Create STL unordered_map<int, int> prnt prnt[root->data] = root->data Loop While !que.empty() temp = que.front() que.pop() IF !temp->left && !temp->right leaf = temp->data break End Else IF temp->left que.push(temp->left) prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data End IF temp->right que.push(temp->right) prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data End End End path(leaf, prnt) print leaf Step 5 -> In main() Create tree using Node* root = newnode(90) root->left = newnode(21) call left(root) stop
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
struct Node *left,*right;
int data;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
//function to set a path
void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) {
if (prnt[data] == data)
return;
path(prnt[data], prnt);
cout << prnt[data] << " ";
}
//function for a leaf path
void left(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int leaf = -1;
Node* temp = NULL;
unordered_map<int, int> prnt;
prnt[root->data] = root->data;
while (!que.empty()){
temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right{
leaf = temp->data;
break;
} else {
if (temp->left){
que.push(temp->left);
prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data;
}
if (temp->right){
que.push(temp->right);
prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data;
}
}
}
path(leaf, prnt);
cout << leaf << " ";
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(90);
root->left = newnode(21);
root->right = newnode(32);
root->left->left = newnode(45);
root->right->left = newnode(52);
root->right->right = newnode(27);
root->left->left->left = newnode(109);
root->left->left->right = newnode(101);
root->right->right->left = newnode(78);
left(root);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau
90 32 52
