Với cây nhị phân, chương trình phải tìm ra nhiều đường dẫn từ gốc đến lá, có nghĩa là tất cả các đường phải được in ra nhưng thách thức là không sử dụng đệ quy.
Chúng ta sẽ duyệt cây theo cách lặp đi lặp lại vì điều kiện ràng buộc là thực hiện nó mà không cần đệ quy. Vì vậy, để đạt được điều này, chúng ta có thể sử dụng bản đồ STL sẽ lưu trữ phần tử gốc và bất cứ khi nào nút lá được xác định thông qua trình duyệt thứ tự mức, nó sẽ in đường dẫn từ gốc đến lá vì có một con trỏ bản đồ đang trỏ đến nút gốc.
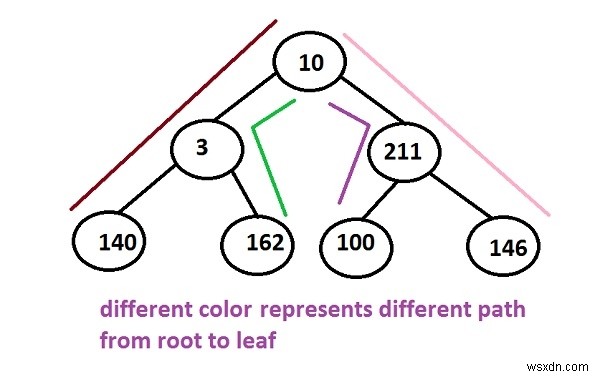
Trong cây ở trên, có nhiều con đường có thể được tạo ra để đi từ gốc đến lá -
10 -> 3 -> 140 10 -> 3 -> 162 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
Do đó, chương trình phải in tất cả các đường dẫn đã cho dưới dạng đầu ra của cây nhị phân đã cho.
Thuật toán
START Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct Node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node->data = data node->left = node->right = NULL; return (node) Step 3 -> create function to calculate the path void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first) create STL stack<Node*> stk Loop While (curr) stk.push(curr) curr = first[curr] End Loop While !stk.empty() curr = stk.top() stk.pop() print curr->data End Step 4 -> create function to find the leaf nodes void leaf(Node* root) IF root = NULL Return End Create STL stack<Node*> stc stc.push(root) Create STL map<Node*, Node*> prnt prnt[root] = NULL Loop while !stc.empty() Node* curr = stc.top() stc.pop() IF!(curr->left) && !(curr->right) calculatePath(curr, prnt) End IF curr->right prnt[curr->right] = curr stc.push(curr->right) End IF curr->left prnt[curr->left] = curr stc.push(curr->left) End End STOP
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure of a node
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data){
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//this function will calculate the path
void calculatePath(Node* curr, map<Node*, Node*> first){
stack<Node*> stk;
while (curr){
stk.push(curr);
curr = first[curr];
}
while (!stk.empty()){
curr = stk.top();
stk.pop();
cout << curr->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//this function will lead to the leafs
void leaf(Node* root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
stack<Node*> stc;
stc.push(root);
map<Node*, Node*> prnt;
prnt[root] = NULL;
while (!stc.empty()){
Node* curr = stc.top();
stc.pop();
if (!(curr->left) && !(curr->right))
calculatePath(curr, prnt);
if (curr->right){
prnt[curr->right] = curr;
stc.push(curr->right);
}
if (curr->left){
prnt[curr->left] = curr;
stc.push(curr->left);
}
}
}
int main(){
Node* root = newNode(67); //it will insert the nodes to create a tree
root->left = newNode(34);
root->right = newNode(89);
root->left->left = newNode(23);
root->left->right = newNode(95);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
leaf(root); //call the function leaf
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau
67 34 23 67 34 95 67 89 12
