Chúng tôi được cung cấp với đồ thị vô hướng cũng như không có trọng số làm đầu vào và nhiệm vụ là tìm sản phẩm của các chu kỳ được hình thành trong giá trị đã cho và hiển thị kết quả.
Ví dụ
Đầu vào
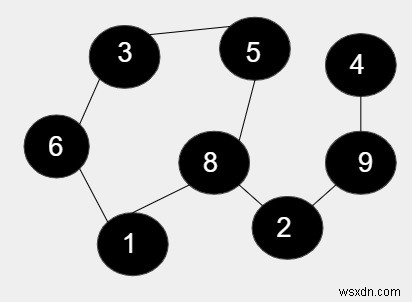
Trong hình đã cho, có 8 nút và trong số 5 nút đó đang hình thành chu kỳ bao gồm 1, 6, 3, 5, 8 và phần còn lại của nút không được bao gồm trong chu kỳ. Vì vậy, độ dài của chu kỳ là 5 vì nó bao gồm 5 nút, do đó sản phẩm là 5
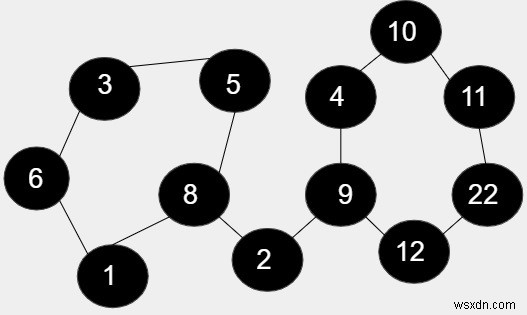
Trong hình đã cho, có 12 nút và trong số đó 11 (5 +6) nút đang hình thành chu kỳ bao gồm 1, 6, 3, 5, 8 và 9, 4, 10, 11, 22, 12 và phần còn lại của nút 2 không được bao gồm trong chu kỳ. Vì vậy, độ dài của chu kỳ là 5 * 6 =30
Phương pháp tiếp cận được sử dụng trong chương trình dưới đây như sau -
- Nhập các nút để hình thành chu trình
- Tạo hàm DFS và gọi hàm này để đi qua đỉnh bằng cách tô màu cho nó
- Nút được đánh dấu là đã truy cập hoàn toàn hoặc đã truy cập một phần
- Nút đã truy cập hoàn toàn không cần phải truy cập lại và do đó không cần lưu trữ trong khi các nút đã truy cập một phần cần được lưu trữ vì chúng được truy cập lại
- In kết quả
Thuật toán
Start Step 1-> declare function to traverse the graph using DFS approach void DFS(int i, int j, int color[], int highlight[], int parent[], int& number) IF color[i] = 2 Return End IF color[i] = 1 Set number++ Declare and set int temp = j Set highlight[temp] = number Loop While temp != i Set temp = parent[temp] Set highlight[temp] = number End Return End Set parent[i] = j Set color[i] = 1 For int k : graph[i] IF k = parent[i] Continue End Call DFS(k, i, color, highlight, parent, number) End Set color[i] = 2 Step 2-> declare function to find product of nodes in cycle int product(int edge, int highlight[], int& number) call unordered_map<int, int> mp Loop For i = 1 and i <= edge and i++ IF (highlight[i] != 0) Set mp[highlight[i]]++ End End Declare and set int temp = 1 Loop For i = 1 and i <= number and i++ Set temp = temp * mp[i] End IF number = 0 Set temp = 0 End return temp Step 3-> In main() Call function as insert(1, 2) to insert a node Declare int color[size], parent[size] Declare int highlight[size] Declare and set int number = 0 Declare and set int edge = 10 Call DFS(1, 0, color, highlight, parent, number) Call print function as product(edge, highlight, number) Stop
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int size = 100000;
vector<int> graph[size];
//function to traverse the graph using DFS approach
void DFS(int i, int j, int color[], int highlight[], int parent[], int& number) {
// for travered node
if (color[i] == 2) {
return;
}
//not completely visited
if (color[i] == 1) {
number++;
int temp = j;
highlight[temp] = number;
//for backtracking the vertex
while (temp != i) {
temp = parent[temp];
highlight[temp] = number;
}
return;
}
parent[i] = j;
color[i] = 1;
for (int k : graph[i]) {
if (k == parent[i]) {
continue;
}
DFS(k, i, color, highlight, parent, number);
}
color[i] = 2;
}
// function for inserting edges to graph
void insert(int u, int v) {
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Find product of nodes in cycle
int product(int edge, int highlight[], int& number) {
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= edge; i++) {
if (highlight[i] != 0)
mp[highlight[i]]++;
}
int temp = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
temp = temp * mp[i];
}
if (number == 0)
temp = 0;
return temp;
}
int main() {
//for inserting a node in the graph
insert(1, 2);
insert(2, 3);
insert(3, 4);
insert(4, 6);
insert(4, 7);
insert(5, 6);
insert(3, 5);
insert(7, 8);
insert(6, 10);
insert(5, 9);
insert(10, 11);
int color[size], parent[size];
int highlight[size];
int number = 0;
int edge = 10;
DFS(1, 0, color, highlight, parent, number);
// function to print the cycles
cout<<"product of all the nodes in the cycle is :"<< product(edge, highlight, number);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
Product of all the nodes in the cycle is :4
