Giả sử chúng ta có một cây nhị phân, chúng ta phải tìm cùng một cây nhưng giá trị của mọi nút được thay thế bằng giá trị của nó + tất cả các tổng của cây con trái và phải của nó.
Vì vậy, nếu đầu vào giống như
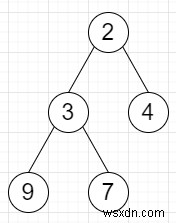
thì đầu ra sẽ là
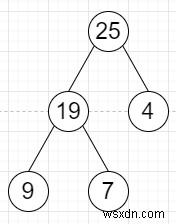
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng tôi sẽ làm theo các bước sau -
-
Định nghĩa một hàm tree_sum (). Điều này sẽ bén rễ của một cái cây
-
nếu root là null thì
-
trả về 0
-
-
dữ liệu của root:=tree_sum (bên trái của root) + tree_sum (bên phải của root) + dữ liệu của root
-
trả về dữ liệu của root
-
Từ phương thức chính, hãy thực hiện như sau:
-
tree_sum (gốc)
-
trả về thư mục gốc
Hãy cùng chúng tôi xem cách triển khai sau để hiểu rõ hơn -
Ví dụ
class TreeNode: def __init__(self, data, left = None, right = None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right def inorder(root): if root: inorder(root.left) print(root.data, end = ', ') inorder(root.right) class Solution: def solve(self, root): def tree_sum(root: TreeNode): if root is None: return 0 root.data = tree_sum(root.left) + tree_sum(root.right) + root.data return root.data tree_sum(root) return root ob = Solution() root = TreeNode(2) root.left = TreeNode(3) root.right = TreeNode(4) root.left.left = TreeNode(9) root.left.right = TreeNode(7) ob.solve(root) inorder(root)
Đầu vào
root = TreeNode(12) root.left = TreeNode(8) root.right = TreeNode(15) root.left.left = TreeNode(3) root.left.right = TreeNode(10)
Đầu ra
9, 19, 7, 25, 4,
