Trong một số trường hợp, chúng tôi không nên cho phép ứng dụng chạy trên các thiết bị đã root cho cổng thanh toán. Ví dụ này trình bày cách xác định xem có chạy trên thiết bị đã root hay không.
Bước 1 - Tạo một dự án mới trong Android Studio, đi tới Tệp ⇒ Dự án Mới và điền tất cả các chi tiết cần thiết để tạo một dự án mới.
Bước 2 - Thêm mã sau vào res / layout / activity_main.xml.
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id = "@+id/parent" xmlns:tools = "http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "match_parent" tools:context = ".MainActivity" android:gravity = "center" android:orientation = "vertical"> <TextView android:id = "@+id/rootFinder" android:layout_margin = "20dp" android:textAlignment = "center" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
Trong đoạn mã trên, chúng ta đã có một chế độ xem văn bản. Nó chứa thông tin về root.
Bước 3 - Thêm mã sau vào src / MainActivity.java
package com.example.andy.myapplication;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.RequiresApi;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
int view = R.layout.activity_main;
TextView rootFinder;
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN)
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(view);
rootFinder = findViewById(R.id.rootFinder);
executeShellCommand("su");
}
private void executeShellCommand(String su) {
Process process = null;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(su);
rootFinder.setText("It is rooted device");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "It is rooted device", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
rootFinder.setText("It is not rooted device");
} finally {
if (process ! = null) {
try {
process.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) { }
}
}
}
} Trong đoạn mã trên, chúng tôi đang kiểm tra thiết bị đã được root hay chưa và thêm văn bản vào chế độ xem văn bản. Để kiểm tra thiết bị Android đã được root hay chưa, hãy sử dụng đoạn mã sau-
executeShellCommand("su");
..........................................................................................
private void executeShellCommand(String su) {
Process process = null;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(su);
rootFinder.setText("It is rooted device");
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "It is rooted device", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
rootFinder.setText("It is not rooted device");
} finally {
if (process ! = null) {
try {
process.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) { }
}
}
} Hãy thử chạy ứng dụng của bạn. Tôi giả sử bạn đã kết nối thiết bị Di động Android thực tế với máy tính của mình. Để chạy ứng dụng từ android studio, hãy mở một trong các tệp hoạt động của dự án của bạn và nhấp vào biểu tượng Chạy từ thanh công cụ. Chọn thiết bị di động của bạn làm tùy chọn, sau đó kiểm tra thiết bị di động sẽ hiển thị màn hình mặc định của bạn -
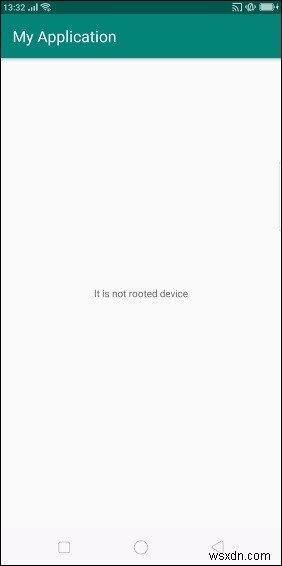
Trong kết quả ở trên được hiển thị, thiết bị ra ngoài chưa được root.
