Trong phần này, chúng ta sẽ thấy kỹ thuật duyệt theo thứ tự cấp độ cho cây tìm kiếm nhị phân.
Giả sử chúng ta có một cây như thế này -
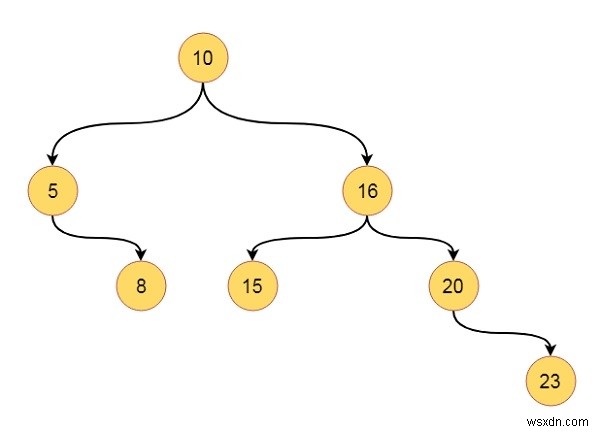
Trình tự duyệt sẽ như sau:10, 5, 16, 8, 15, 20, 23
Thuật toán
levelOrderTraverse(root): Begin define queue que to store nodes insert root into the que. while que is not empty, do item := item present at front position of queue print the value of item if left of the item is not null, then insert left of item into que end if if right of the item is not null, then insert right of item into que end if delete front element from que done End
Ví dụ
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class node{
public:
int h_left, h_right, bf, value;
node *left, *right;
};
class tree{
private:
node *get_node(int key);
public:
node *root;
tree(){
root = NULL; //set root as NULL at the beginning
}
void levelorder_traversal(node *r);
node *insert_node(node *root, int key);
};
node *tree::get_node(int key){
node *new_node;
new_node = new node; //create a new node dynamically
new_node->h_left = 0; new_node->h_right = 0;
new_node->bf = 0;
new_node->value = key; //store the value from given key
new_node->left = NULL; new_node->right = NULL;
return new_node;
}
void tree::levelorder_traversal(node *root){
queue <node*> que;
node *item;
que.push(root); //insert the root at first
while(!que.empty()){
item = que.front(); //get the element from the front end
cout << item->value << " ";
if(item->left != NULL) //When left child is present, insert into queue
que.push(item->left);
if(item->right != NULL) //When right child is present, insert into queue
que.push(item->right);
que.pop(); //remove the item from queue
}
}
node *tree::insert_node(node *root, int key){
if(root == NULL){
return (get_node(key)); //when tree is empty, create a node as root
}
if(key < root->value){ //when key is smaller than root value, go to the left
root->left = insert_node(root->left, key);
} else if(key > root->value) { //when key is greater than root value, go to the right
root->right = insert_node(root->right, key);
}
return root; //when key is already present, do not insert it again
}
main(){
node *root;
tree my_tree;
//Insert some keys into the tree.
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 10);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 5);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 16);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 20);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 15);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 8);
my_tree.root = my_tree.insert_node(my_tree.root, 23);
cout << "Level-Order Traversal: ";
my_tree.levelorder_traversal(my_tree.root);
} Đầu ra
Level-Order Traversal: 10 5 16 8 15 20 23
