Ở đây chúng ta sẽ xem cách thực hiện xóa một nút khỏi B-Tree. Giả sử chúng ta có một BTree như bên dưới -
Ví dụ về B-Tree -
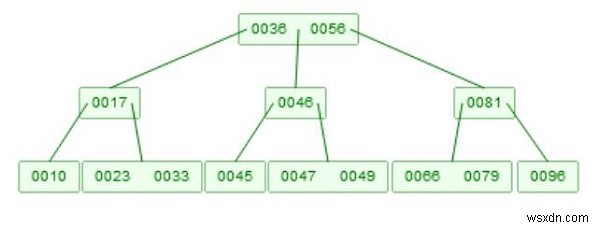
Xóa có hai phần. Lúc đầu, chúng ta phải tìm phần tử. Chiến lược đó giống như truy vấn. Bây giờ để xóa, chúng ta phải quan tâm đến một số quy tắc. Một nút phải có ít nhất m / 2 phần tử. Vì vậy, nếu chúng ta xóa, một phần tử và nó chỉ còn lại ít hơn m-1 phần tử, thì nó sẽ tự điều chỉnh. Nếu toàn bộ nút bị xóa, thì nút con của nó sẽ được hợp nhất và nếu kích thước của chúng là m, thì hãy chia chúng thành hai phần và một lần nữa giá trị trung bình sẽ tăng lên.
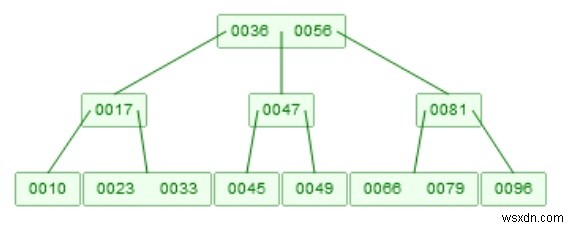
Giả sử chúng ta muốn xóa 46. Bây giờ có hai con. [45], và [47, 49], sau đó chúng sẽ được hợp nhất, nó sẽ là [45, 47, 49], bây giờ 47 sẽ tăng lên.
Thuật toán
BTreeDelete (x, key) -
Đầu vào - Gốc của cây và khóa để xóa
Chúng tôi sẽ giả định rằng khóa có trong danh sách
if x is leaf, then delete object with key ‘key’ from x else if x does not contain the object with key ‘key’, then locate the child x->child[i] whose key range is holding ‘key’ y := x->child[i] if y has m/2 elements, then If the sibling node z immediate to the left or right of y, has at least one more object than m/2, add one more object by moving x->key[i] from x to y, and move that last or first object from z to x. If y is non-leaf node, then last or first child pointer in z is also moved to y else any immediate sibling of y has m/2 elements, merge y with immediate sibling end if BTreeDelete(y, key) else if y that precedes ‘key’ in x, has at-least m/2 + 1 objects, then find predecessor k of ‘key’, in the sub-tree rooted by y. then recursively delete k from the sub-tree and replace key with k in x else if ys has m/2 elements, then check the child z, which is immediately follows ‘key’ in x if z has at least m/2+1 elements, then find successor k of ‘key’, in the sub-tree rooted by z. recursively delete k from sub-tree, and replace key with k in x else both y and z has m/2 elements, then merge then into one node, and push ‘key’ down to the new node as well. Recursively delete ‘key’ from this new node end if end if
