Để xây dựng các điểm dữ liệu mới trong một phạm vi của một tập hợp điểm dữ liệu đã cho rời rạc, kỹ thuật nội suy được sử dụng. Kỹ thuật nội suy Lagrange là một trong số đó. Khi các điểm dữ liệu đã cho không phân bố đều, chúng ta có thể sử dụng phương pháp nội suy này để tìm lời giải. Đối với phép nội suy Lagrange, chúng ta phải tuân theo phương trình này.
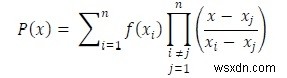
Đầu vào và Đầu ra
Input:
List of x and f(x) values. find f(3.25)
x: {0,1,2,3,4,5,6}
f(x): {0,1,8,27,64,125,216}
Output:
Result after Lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281 Thuật toán
largrangeInterpolation(x: array, fx: array, x1)
Đầu vào - mảng x và mảng fx để lấy dữ liệu đã biết trước đó và điểm x1.
Đầu ra: Giá trị của f (x1).
Begin res := 0 and tempSum := 0 for i := 1 to n, do tempProd := 1 for j := 1 to n, do if i ≠ j, then tempProf := tempProd * (x1 – x[j])/(x[i] – x[j]) done tempPord := tempProd * fx[i] res := res + tempProd done return res End
Ví dụ
#include<iostream>
#define N 6
using namespace std;
double lagrange(double x[], double fx[], double x1) {
double res = 0, tempSum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<=N; i++) {
double tempProd = 1; //for each iteration initialize temp product
for(int j = 1; j<=N; j++) {
if(i != j) { //if i = j, then denominator will be 0
tempProd *= (x1 - x[j])/(x[i] - x[j]); //multiply each term using formula
}
}
tempProd *= fx[i]; //multiply f(xi)
res += tempProd;
}
return res;
}
main() {
double x[N+1] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6};
double y[N+1] = {0,1,8,27,64,125,216};
double x1 = 3.25;
cout << "Result after lagrange interpolation f("<<x1<<") = " << lagrange(x, y, x1);
} Đầu ra
Result after lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281
