Máy tính là một máy điện tử có thể thực hiện nhiều phép toán số học và logic. Để thực hiện tất cả các chức năng nâng cao, máy tính cần sức mạnh của các đơn vị xử lý có thể xử lý tất cả các chức năng phức tạp do người dùng thực hiện. Vì vậy, nếu bạn chuẩn bị mua một hệ thống máy tính mới và đang băn khoăn không biết bộ xử lý trung tâm nào sẽ tốt cho thiết bị của mình, thì chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên đọc về CPU và công dụng của CPU.
CPU (Bộ xử lý trung tâm) là gì?
Còn được gọi luân phiên là bộ xử lý, bộ xử lý trung tâm hoặc bộ vi xử lý, CPU là bộ xử lý chính của máy tính. Trách nhiệm của CPU máy tính là chạy trơn tru các hướng dẫn giữa phần cứng và phần mềm để chúng có thể hoạt động mà không gặp bất kỳ sự cố nào. Nó còn được gọi là bộ não của hệ thống máy tính vì tất cả các chức năng quan trọng như thực hiện tính toán, chạy chương trình và xử lý nhiều hoạt động đều do CPU quản lý.
Bộ xử lý được đặt và cố định vào đế cắm CPU tương thích được lưu trữ trong bo mạch chủ. Nhiệt được tạo ra bởi bộ xử lý, đó là lý do tại sao chúng được bao phủ bởi bộ tản nhiệt để bảo vệ sự tỏa nhiệt. Chip CPU có hình chữ nhật để có thể dễ dàng cất giữ trong đế cắm. Ở mặt dưới của con chip là hàng trăm chân cắm cắm vào từng lỗ tương ứng trong ổ cắm.
Ngày nay, tất cả các CPU đều rất giống nhau về thiết kế và chức năng. Tuy nhiên, Intel và AMD có chip lớn hơn có thể được lưu trữ trên bo mạch chủ. Hơn nữa, có rất nhiều ổ cắm khác nhau có sẵn trên bo mạch chủ và mỗi ổ cắm có cách bố trí khác nhau và có một chức năng cụ thể để lưu trữ bộ xử lý.
Các thành phần của CPU
Bộ xử lý máy tính đầu tiên được giới thiệu bởi nhà thiết kế intel tên là Ted Hoff vào những năm 1970. Bộ xử lý đầu tiên được Intel gọi là 4004. Về cơ bản, bộ xử lý máy tính bao gồm các thành phần khác nhau sau đây –
- Bộ nhớ hoặc Đơn vị lưu trữ
- Bộ điều khiển
- ALU(Đơn vị logic số học)
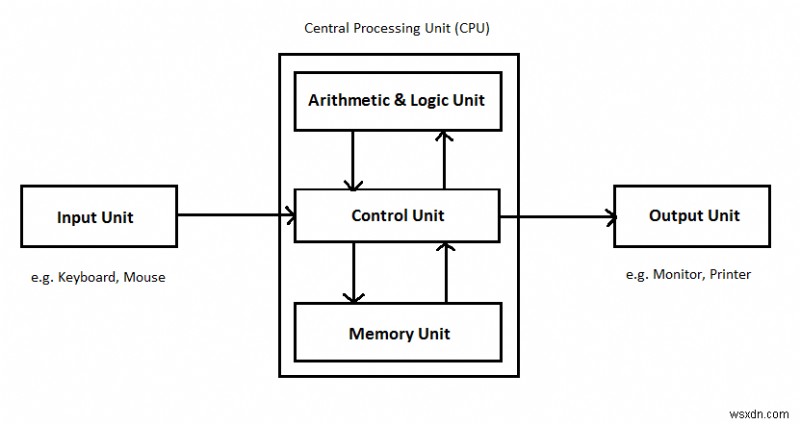
Đơn vị logic số học (ALU)
Đơn vị logic số học thực hiện các chức năng toán học, logic và trợ giúp trong quá trình ra quyết định. Đơn vị này bao gồm hai tiểu mục là,
- Phần số học: Chức năng của phần số học là thực hiện các phép tính số học như cộng, trừ, nhân và chia. Tất cả các thao tác phức tạp được thực hiện bằng cách sử dụng lặp đi lặp lại các thao tác trên.
- Phần logic: Chức năng của phần logic là thực hiện các thao tác logic như so sánh, chọn, đối sánh và hợp nhất dữ liệu.
Bộ điều khiển (CU)
Bộ điều khiển trích xuất các lệnh từ bộ nhớ, giải mã và thực thi chúng, gọi ALU khi cần thiết.
Các chức năng của đơn vị này là –
- Nó chịu trách nhiệm kiểm soát việc truyền dữ liệu và hướng dẫn giữa các đơn vị khác của máy tính.
- Nó quản lý và điều phối tất cả các đơn vị của máy tính.
- Nó nhận các hướng dẫn từ bộ nhớ, diễn giải chúng và điều khiển hoạt động của máy tính.
- Nó giao tiếp với các thiết bị Đầu vào/Đầu ra để truyền dữ liệu hoặc kết quả từ bộ lưu trữ.
- Nó không xử lý hoặc lưu trữ dữ liệu.
Bộ nhớ hoặc Đơn vị lưu trữ
Đơn vị này có thể lưu trữ hướng dẫn, dữ liệu và kết quả trung gian. Đơn vị này cung cấp thông tin cho các đơn vị khác của máy tính khi cần thiết. Nó còn được gọi là bộ nhớ trong hoặc bộ nhớ chính hoặc bộ lưu trữ chính hoặc Bộ nhớ Truy cập Ngẫu nhiên (RAM).
Kích thước của nó ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ, sức mạnh và khả năng. Bộ nhớ chính và bộ nhớ phụ là hai loại bộ nhớ trong máy tính. Các chức năng của đơn vị bộ nhớ là –
- Nó lưu trữ tất cả dữ liệu và hướng dẫn cần thiết để xử lý.
- Nó lưu trữ các kết quả xử lý trung gian.
- Nó lưu trữ kết quả xử lý cuối cùng trước khi các kết quả này được đưa ra thiết bị đầu ra.
- Tất cả đầu vào và đầu ra được truyền qua bộ nhớ chính.
Lịch sử của CPU
Theo dòng lịch sử, tốc độ và hiệu suất của bộ xử lý trung tâm đã phát triển vượt bậc. CPU đầu tiên được giới thiệu bởi Intel 4004 được phát hành vào ngày 15 tháng 11 năm 1971, có 2.300 bóng bán dẫn và thực hiện 60.000 phép tính mỗi giây. Và, bạch kim mới nhất của Intel ngày nay cung cấp 3.300.000 bóng bán dẫn và thực hiện khoảng 188.000.000 lệnh mỗi giây. Bạn có thể dễ dàng so sánh sự khác biệt giữa hiệu suất và tốc độ của cả hai đơn vị CPU.
Ai là người sáng lập ra CPU?
CPU đầu tiên là Intel 4004 được Intel phát hành vào năm 1971. Federico Faggin là nhà thiết kế chính của CPU thương mại đầu tiên . Anh ấy là một trong những người được ghi nhận chính là người đã phát minh ra CPU.| Năm | Đã giới thiệu bộ xử lý máy tính |
| 1823 | Nam tước Jons Jackob Berzelius khám phá ra silicon (Si), ngày nay là thành phần cơ bản của bộ xử lý. |
| 1903 | Nikola Tesla đã cấp bằng sáng chế cho các mạch logic điện được gọi là “cổng” hoặc “công tắc” vào năm 1903. |
| 1947 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley invent the first transistor at the Bell Laboratories on December 23, 1947. |
| 1948 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley patent the first transistor in 1948. |
| 1956 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for their work on the transistor. |
| 1958 | The first integrated circuit was first developed by Robert Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor and Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments. The first IC was demonstrated on September 12, 1958. |
| 1960 | IBM developed the first automatic mass-production facility for transistors in New York in 1960. |
| 1968 | Intel Corporation was founded by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore in 1968. |
| 1969 | AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) was founded on May 1, 1969. |
| 1971 | Intel with the help of Ted Hoff introduced the first microprocessor, the Intel 4004 on November 15, 1971. The 4004 had 2,300 transistors, performed 60,000 OPS (operations per second), addressed 640 bytes of memory, and cost $200.00. |
| 1972 | Intel introduced the 8008 processor on April 1, 1972. |
| 1974 | Intel’s improved microprocessor chip was introduced on April 1, 1974; the 8080 became a standard in the computer industry. |
| 1976 | Intel introduced the 8085 processor in March 1976. |
| 1976 | The Intel 8086 was introduced on June 8, 1976. |
| 1979 | The Intel 8088 was released on June 1, 1979. |
| 1979 | The Motorola 68000, a 16/32-bit processor was released and was later chosen as the processor for the Apple Macintosh and Amiga computers. |
| 1982 | The Intel 80286 was introduced on February 1, 1982. |
| 1985 | Intel introduced the first 80386 in October 1985. |
| 1987 | The SPARC processor was first introduced by Sun. |
| 1988 | Intel 80386SX was introduced in 1988. |
| 1991 | AMD introduced the AM386 microprocessor family in March 1991. |
| 1991 | Intel introduced the Intel 486SX chip in April in efforts to help bring a lower-cost processor to the PC market selling for $258.00. |
| 1992 | Intel released the 486DX2 chip on March 2, 1992, with a clock doubling ability that generates higher operating speeds. |
| 1993 | Intel released the Pentium processor on March 22, 1993. The processor was a 60 MHz processor, incorporates 3.1 million transistors and sells for $878.00. |
| 1994 | Intel released the second generation of Intel Pentium processors on March 7, 1994. |
| 1995 | Intel introduced the Intel Pentium Pro in November 1995. |
| 1996 | Intel announced the availability of the Pentium 150 MHz with 60 MHz bus and 166 MHz with 66 MHz bus on January 4, 1996. |
| 1996 | AMD introduced the K5 processor on March 27, 1996, with speeds of 75 MHz to 133 MHz and bus speeds of 50 MHz, 60 MHz, or 66 MHz. The K5 was the first processor developed completely in-house by AMD. |
| 1997 | AMD released their K6 processor line in April 1997, with speeds of 166 MHz to 300 MHz and a 66 MHz bus speed. |
| 1997 | Intel Pentium II was introduced on May 7, 1997. |
| 1998 | AMD introduced their new K6-2 processor line on May 28, 1998, with speeds of 266 MHz to 550 MHz and bus speeds of 66 MHz to 100 MHz. The K6-2 processor was an enhanced version of AMD’s K6 processor. |
| 1998 | Intel released the first Xeon processor, the Pentium II Xeon 400 (512 K or 1 M cache, 400 MHz, 100 MHz FSB) in June 1998. |
| 1999 | Intel released the Celeron 366 MHz and 400 MHz processors on January 4, 1999. |
| 1999 | AMD released its K6-III processors on February 22, 1999, with speeds of 400 MHz or 450 MHz and bus speeds of 66 MHz to 100 MHz. It also featured an on-die L2 cache. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 500 MHz was released on February 26, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 550 MHz was released on May 17, 1999. |
| 1999 | AMD introduced the Athlon processor series on June 23, 1999. The Athlon would be produced for the next six years in speeds ranging from 500 MHz up to 2.33 GHz. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 600 MHz was released on August 2, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 533B and 600B MHz was released on September 27, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III Coppermine series was first introduced on October 25, 1999. |
| 2000 | On January 5, 2000, AMD released the 800 MHz Athlon processor. |
| 2000 | Intel released the Celeron 533 MHz with a 66 MHz bus processor on January 4, 2000. |
| 2000 | AMD first released the Duron processor on June 19, 2000, with speeds of 600 MHz to 1.8 GHz and bus speeds of 200 MHz to 266 MHz. The Duron was built on the same K7 architecture as the Athlon processor. |
| 2000 | Intel announces on August 28th that it will recall its 1.3 GHz Pentium III processors due to a glitch. Users with these processors should contact their vendors for additional information about the recall. |
| 2001 | On January 3, 2001, Intel released the 800 MHz Celeron processor with a 100 MHz bus. |
| 2001 | On January 3, 2001, Intel released the 1.3 GHz Pentium 4 processor. |
| 2001 | AMD announced a new branding scheme on October 9, 2001. Instead of identifying processors by their clock speed, the AMD Athlon XP processors will bear monikers of 1500+, 1600+, 1700+, 1800+, 1900+, 2000+, etc. Each higher model number will represent a higher clock speed. |
| 2002 | Intel released the Celeron 1.3 GHz with a 100 MHz bus and 256 kB of level 2 cache. |
| 2003 | Intel Pentium M was introduced in March 2003. |
| 2003 | AMD released the first single-core Opteron processors, with speeds of 1.4 GHz to 2.4 GHz and 1024 KB L2 cache, on April 22, 2003. |
| 2003 | AMD released the first Athlon 64 processors, the 3200+, and the first Athlon 64 FX processor, the FX-51, on September 23, 2003. |
| 2004 | AMD released the first Sempron processor on July 28, 2004, with a 1.5 GHz to 2.0 GHz clock speed and 166 MHz bus speed. |
| 2005 | AMD released their first dual-core processor, the Athlon 64 X2 3800+ (2.0 GHz, 512 KB L2 cache per core), on April 21, 2005. |
| 2006 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E6320 (4 M cache, 1.86 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on April 22, 2006. |
| 2006 | Intel introduced the Intel Core 2 Duo processors with the Core 2 Duo processor E6300 (2 M cache, 1.86 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on July 27, 2006. |
| 2006 | Intel introduced the Intel Core 2 Duo processor for the laptop computer with the Core 2 Duo processor T5500, as well as other Core 2 Duo T series processors, in August 2006. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q6600 (8 M cache, 2.40 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) in January 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4300 (2 M cache, 1.80 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on January 21, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q6700 (8 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) in April 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4400 (2 M cache, 2.00 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on April 22, 2007. |
| 2007 | AMD renamed the Athlon 64 X2 processor line to Athlon X2 and released the first in that line, the Brisbane series (1.9 to 2.6 GHz, 512 KB L2 cache) on June 1, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4500 (2 M cache, 2.20 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on July 22, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4600 (2 M cache, 2.40 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on October 21, 2007. |
| 2007 | AMD released the first Phenom X4 processors (2 M cache, 1.8 GHz to 2.6 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on November 19, 2007. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q9300 and the Core 2 Quad processor Q9450 in March 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4700 (2 M cache, 2.60 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on March 2, 2008. |
| 2008 | AMD released the first Phenom X3 processors (2 M cache, 2.1 GHz to 2.5 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on March 27, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the first of the Intel Atom series of processors, the Z5xx series, in April 2008. They are single-core processors with a 200 MHz GPU. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7200 (3 M cache, 2.53 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on April 20, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7300 (3 M cache, 2.66 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on August 10, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released several Core 2 Quad processors in August 2008:the Q8200, the Q9400, and the Q9650. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7400 (3 M cache, 2.80 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on October 19, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the first Core i7 desktop processors in November 2008:the i7-920, the i7-940, and the i7-965 Extreme Edition. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X4 (quad-core) processors (6 M cache, 2.5 to 3.7 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on January 8, 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7500 (3 M cache, 2.93 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on January 18, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X3 (triple core) processors (6 M cache, 2.5 to 3.0 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on February 9, 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q8400 (4 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB) in April 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7600 (3 M cache, 3.06 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on May 31, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X2 (dual-core) processors (1024KB L2 cache, 1.6 to 3.5 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) in June 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X2 (dual-core) processors (6 M cache, 3.0 to 3.5 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on June 1, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X4 (quad-core) processors (512 KB L2 cache, 2.2 to 3.1 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) in September 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the first Core i7 mobile processor, the i7-720QM, in September 2009. It uses the Socket G1 socket type, runs at 1.6 GHZ, and features 6 MB L3 cache. |
| 2009 | Intel released the first Core i5 desktop processor with four cores, the i5-750 (8 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB), on September 8, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X3 (triple-core) processors in October 2009. |
| 2010 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q9500 (6 M cache, 2.83 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB) in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i5 mobile processors, the i5-430M and the i5-520E in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i5 desktop processor over 3.0 GHz, the i5-650 in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i3 desktop processors, the i3-530, and i3-540 on January 7, 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i3 mobile processors, the i3-330M (3 M cache, 2.13 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) and the i3-350M, on January 7, 2010. |
| 2010 | AMD released the first Phenom II X6 (hex/six core) processors on April 27, 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i7 desktop processor with six cores, the i3-970, in July 2010. It runs at 3.2 GHz and features 12 MB L3 cache. |
| 2011 | Intel released seven new Core i5 processors with four cores, the i5-2xxx series in January 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A4 line, the A4-3300M and the A4-3310MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A6 line, the A6-3400M and the A6-3410MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A8 line, the A8-3500M,the A8-3510MX, and the A8-3530MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processor in their A6 line, the A6-3650 (4 M L2 cache, 2.6 GHz, 1866 MHz FSB) on June 30, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processor in their A8 line, the A8-3850 (4 M L2 cache, 2.9 GHz, 1866 MHz FSB) on June 30, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processors in their A4 line, the A4-3300 and the A4-3400 on September 7, 2011. |
| 2012 | AMD released the first desktop processors in their A10 line, the A10-5700 and the A10-5800K on October 1, 2012. |
| 2013 | AMD released one of their fastest desktop processors to date, the Athlon II X2 280, on January 28, 2013. It has two cores and runs at 3.6 GHz. |
| 2013 | Intel released their first processor to utilize the BGA-1364 socket and feature an Iris Pro Graphics 5200 GPU. Released in June 2013, it runs at 3.2 GHz and has 6 MB of L3 cache. |
| 2014 | AMD introduced the socket AM1 architecture and compatible processors, like the Sempron 2650, in April 2014. |
| 2014 | AMD released their first Pro A series APU processors, the A6 Pro-7050B, A8 Pro-7150B, and A10 Pro-7350B, in June 2014. They feature on or two cores and run at 1.9 GHz to 2.2 GHz. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 7 processors, 1700, 1700X, and 1800X models, on March 2, 2017. They have eight cores, run at 3.0 to 3.6 GHz, and feature 16 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 5 processors, 1400, 1500X, 1600, and 1600X models, on April 11, 2017. They have four to six cores, run at 3.2 to 3.6 GHz, and feature 8 to 16 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first Core i9 desktop processor, the i9-7900X, in June 2017. It uses the LGA 2066 socket, runs at 3.3 GHZ, has 10 cores, and features 13.75 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 3 processors, the Pro 1200 and Pro 1300 models, on June 29, 2017. They have four cores, run at 3.1 to 3.5 GHz, and feature 8 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 12 cores, the Core i9-7920X, in August 2017. It runs at 2.9 GHZ and features 16.50 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first processor with 16 cores, the Ryzen Threadripper 1950X, on August 10, 2017. It runs at 3.4 GHz and features 32 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 14 cores, the Core i9-7940X, in September 2017. It runs at 3.1 GHZ and features 19.25 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 16 cores, the Core i9-7960X, in September 2017. It runs at 2.8 GHZ and features 22 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 18 cores, the Core i9-7980X, in September 2017. It runs at 2.6 GHZ and features 24.75 MB L3 cache. |
| 2018 | Intel released the first Core i9 mobile processor, the i9-8950HK, in April 2018. It uses the BGA 1440 socket, runs at 2.9 GHZ, has six cores, and features 12 MB L3 cache. |
