Giả sử chúng ta có một cây tìm kiếm nhị phân và một đầu vào khác được gọi là val, chúng ta phải kiểm tra xem val có trong cây hay không.
Vì vậy, nếu đầu vào giống như
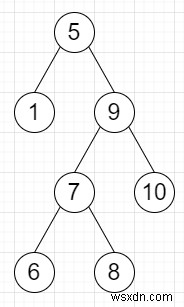
val =7, thì đầu ra sẽ là True, vì 7 có trong cây.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng tôi sẽ làm theo các bước sau−
-
Định nghĩa một hàm giải quyết (). Điều này sẽ bắt đầu, val
-
nếu root là null thì
-
trả về Sai
-
-
nếu dữ liệu của root giống với val, thì
-
trả về True
-
-
nếu dữ liệu của root
-
trả về giải quyết (bên trái của thư mục gốc, val)
-
-
trả về giải quyết (quyền của thư mục gốc, val)
Hãy cùng chúng tôi xem cách triển khai sau để hiểu rõ hơn−
Ví dụ
class TreeNode: def __init__(self, data, left = None, right = None): self.data = data self.left = left self.right = right class Solution: def solve(self, root, val): if not root: return False if root.data == val: return True if root.data > val: return self.solve(root.left, val) return self.solve(root.right, val) ob = Solution() root = TreeNode(5) root.left = TreeNode(1) root.right = TreeNode(9) root.right.left = TreeNode(7) root.right.right = TreeNode(10) root.right.left.left = TreeNode(6) root.right.left.right = TreeNode(8) print(ob.solve(root, 7))
Đầu vào
root = TreeNode(5) root.left = TreeNode(1) root.right = TreeNode(9) root.right.left = TreeNode(7) root.right.right = TreeNode(10) root.right.left.left = TreeNode(6) root.right.left.right = TreeNode(8) 7
Đầu ra
True
