interp1d () chức năng của scipy.interpolate gói được sử dụng để nội suy một hàm 1-D. Cần các mảng giá trị như x và y để gần đúng với một số hàm y =f (x) và sau đó sử dụng phép nội suy để tìm giá trị của các điểm mới.
Cú pháp
scipy.interpolate.interp1d(x, y)
trong đó x là mảng 1-D các giá trị thực và y là mảng N-D các giá trị thực. Độ dài của y dọc theo trục nội suy phải bằng độ dài của x.
Ví dụ 1
Chúng ta hãy xem xét ví dụ sau -
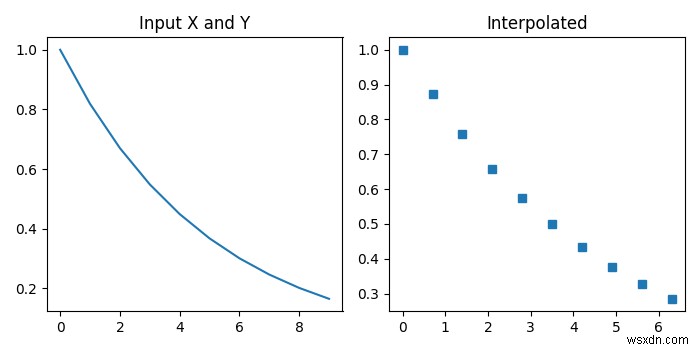
# Import the required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy import interpolate
# Set the figure size
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=[7.00, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"]=True
# Define the values
x = np.arange(0, 10)
y = np.exp(-x/5.0)
# Input Data
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title("Input X and Y")
plt.plot(x,y)
# Interpolated Data
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title("Interpolated")
f = interpolate.interp1d(x, y)
x_new = np.arange(0, 7, 0.7)
y_new = f(x_new)
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, 's')
plt.show() Đầu ra
Chương trình trên sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau -
Ví dụ 2
Hãy để chúng tôi lấy một ví dụ khác -
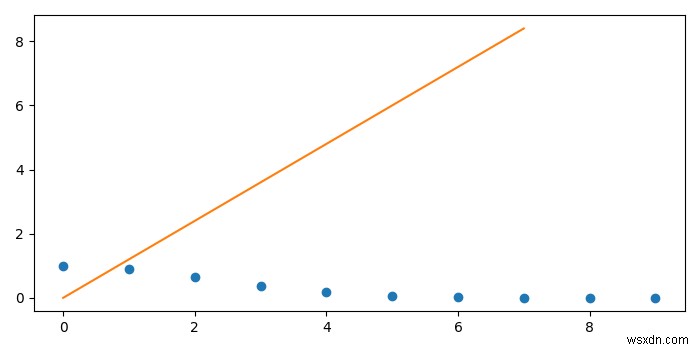
# Import the required libraries import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from scipy import interpolate # Set the figure size plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=[7.00, 3.50] plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"]=True # Define the values x = np.arange(0, 10) y = np.exp(-x **2/9.0) # interpolate function f = interpolate.interp1d(x, y) xnew = np.arange(0, 9, 1.2) plt.plot(x, y, 'o', xnew) plt.show()
Đầu ra
Chương trình trên sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau -