Cho một cây nhị phân với các con bên trái và bên phải và nhiệm vụ là in ra con bên phải và bên trái chính xác của cây đã cho.
Các nút ngoài cùng bên trái là các nút được liên kết ở phía bên trái từ nút cha của cây và các nút ngoài cùng bên phải được liên kết ở phía bên phải từ nút cha của gốc.
Ví dụ
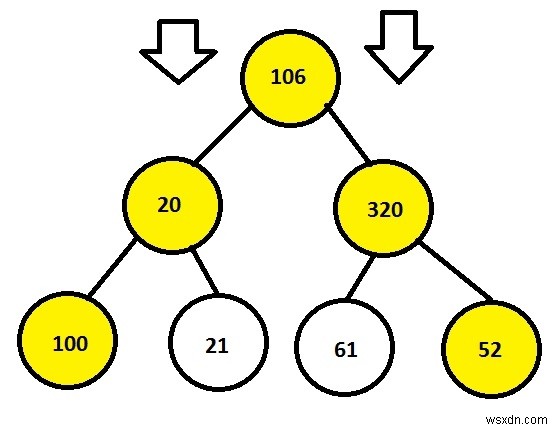
Input: 106 20 320 100 21 61 52 Output: 106 20 320 100 52
Thuật toán
Start Step 1 -> create structure of a node Declare int data Declare struct node *left and *right Step 2 -> create struct node* newNode(int val) Create node* temp=new node Set temp->data = val Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return (temp) step 3 -> Declare Function void print(node *root) IF root == NULL Return Use STL queue<node*> que Call que.push(root) Use STL vector<int> ans Loop While !que.empty() Set int n = que.size() Loop for int i =0 and i<n and i++ Set node *temp = que.front() Set que.pop() IF i=0 Set ans.push_back(temp->data) End Else IF i=n-1 Set ans.push_back(temp->data) End If temp->left Set que.push(temp->left) End IF temp->right Set que.push(temp->right) End End Loop For auto i : ans Print i End Step 4 -> In main() Declare node *root = newNode(106) to create a node Call print(root) stop
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure of a node {
int data;
struct node* left, *right;
};
//structure to create a new node
struct node* newNode(int val){
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = val;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
//function to print corner elements of a tree
void print(node *root) {
if(root == NULL)
return;
queue<node*> que;
que.push(root);
vector<int> ans;
while(!que.empty()){
int n = que.size();
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
node *temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(i==0)
ans.push_back(temp->data);
else if(i==n-1)
ans.push_back(temp->data);
if(temp->left)
que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right)
que.push(temp->right);
}
}
for(auto i : ans)
cout << i << " ";
}
int main (){
node *root = newNode(106);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(320);
root->left->left = newNode(100);
root->left->right = newNode(21);
root->right->left = newNode(61);
root->right->right = newNode(52);
print(root);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau
106 20 320 100 52
