Nhiệm vụ là in các nút bên trái của một cây nhị phân cho trước. Đầu tiên người dùng sẽ chèn dữ liệu do đó tạo ra cây nhị phân và in ra chế độ xem bên trái của cây được hình thành như vậy.
Mỗi nút có thể có nhiều nhất 2 nút con vì vậy ở đây chương trình chỉ phải duyệt qua con trỏ bên trái được liên kết với một nút
Nếu con trỏ trái không rỗng nghĩa là nó sẽ có một số dữ liệu hoặc con trỏ được liên kết với nó nếu không hơn nó sẽ là con bên trái được in và hiển thị dưới dạng đầu ra.
Ví dụ
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
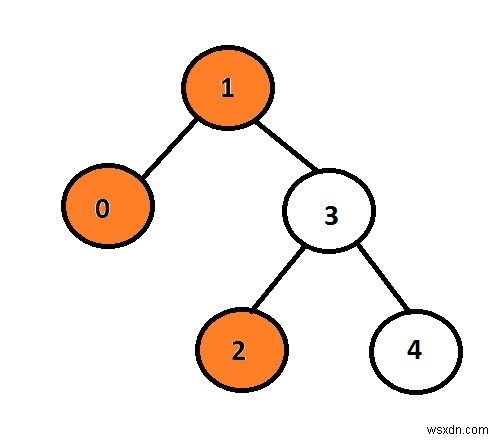
ở đây, các nút màu cam đại diện cho chế độ xem bên trái của cây nhị phân.
Trong hình đã cho nút với dữ liệu 1 là nút gốc vì vậy nó sẽ được in ra hơn là chuyển sang nút con bên trái, nó sẽ in ra 0 và hơn là nó sẽ in ra 3 và in nút con bên trái của nó là 2.
Chúng ta có thể sử dụng phương pháp đệ quy để lưu trữ mức của nút và liên tục chuyển sang mức khác.
Đoạn mã dưới đây cho thấy cách triển khai c của thuật toán đã cho
Thuật toán
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data Declare temp variable of node using malloc Set temp->data = new_data Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return temp Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) IF root = NULL Exit End IF *highest_level < level Print root->data Set *highest_level = level End Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level) Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level) Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root) Set int highest_level = 0 Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level) Step 5-> In main() Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1) Call left(root) STOP
Ví dụ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
} Đầu ra
Nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau.
left view of a binary tree is : 1 0 2
