Cho một mảng có kích thước nxn, chương trình phải in các phần tử của một mảng theo mô hình rắn bắt đầu từ cột cuối cùng có nghĩa là từ phần tử thứ arr [0] [n] mà không thực hiện bất kỳ thay đổi nào đối với vị trí ban đầu của chúng.
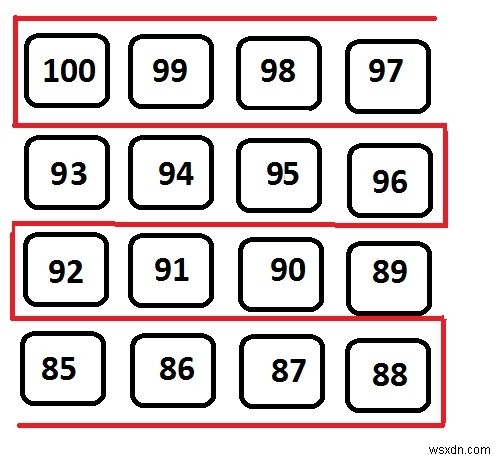
Ví dụ
Input: arr[]= 100 99 98 97 93 94 95 96 92 91 90 89 85 86 87 88 Output: 97 98 99 100 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85
Thuật toán
START Step 1 -> declare initial variable as int n to 5, i and j Step 2 -> declare array of 2-D matrix with elements Step 3 -> Loop For i=0 and i<n and i++ IF i%2==1 Loop For j=0 and j<n and j++ Print arr[i][j] End End Else Loop For j=n-1 and j>=0 and j-- Print arr[i][j] End End STOP
Ví dụ
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int n = 5;
int arr[][5]= {
{10, 20, 30, 40, 50},
{ 60, 70, 80, 90, 100 },
{ 110, 120, 130, 140, 150 },
{ 160, 170, 180, 190, 200 },
{ 210, 220, 230, 240, 250 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //from column as we must start from the end
if (i%2 == 1)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
else
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--)
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau
50 40 30 20 10 60 70 80 90 100 150 140 130 120 110 160 170 180 190 200 250 240 230 220 210
