Giả sử chúng ta có một cây nhị phân hoàn chỉnh, chúng ta phải đếm số lượng nút. Vì vậy, nếu cây như -
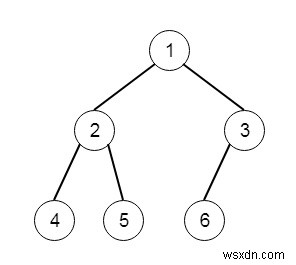
Vì vậy, đầu ra sẽ là 6.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng tôi sẽ làm theo các bước sau
- Điều này sẽ sử dụng phương pháp đệ quy. Phương thức này, countNodes () đang lấy gốc làm đối số.
- hr:=0 và hl:=0
- tạo hai nút l và r làm gốc
- while l không trống
- tăng hl thêm 1
- l:=left of l
- while r không trống
- r:=bên phải của r
- tăng thêm 1 giờ
- nếu hl =hr, thì trả về (2 ^ hl) - 1
- trả về 1 + countNodes (bên trái của thư mục gốc) + countNodes (bên phải của thư mục gốc)
Hãy cùng chúng tôi xem cách triển khai sau để hiểu rõ hơn -
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}else{
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int> v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
class Solution {
public:
int fastPow(int base, int power){
int res = 1;
while(power > 0){
if(power & 1) res *= base;
base *= base;
power >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
int hr = 0;
int hl = 0;
TreeNode* l = root;
TreeNode* r = root;
while(l){
hl++;
l = l->left;
}
while(r){
r = r->right;
hr++;
}
if(hl == hr) return fastPow(2, hl) - 1;
return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
};
main(){
Solution ob;
vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
TreeNode *node = make_tree(v);
cout << (ob.countNodes(node));
} Đầu vào
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
Đầu ra
10
