Giả sử chúng ta có một cây nhị phân; chúng ta phải tìm tổng giá trị của các lá sâu nhất của nó. Vì vậy, nếu cây như -
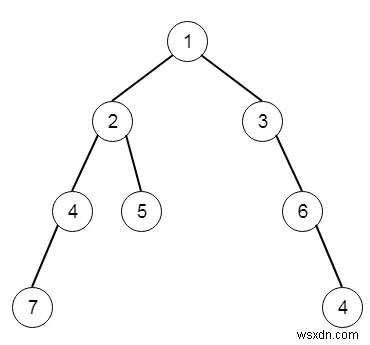
Khi đó đầu ra sẽ là 11.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng tôi sẽ làm theo các bước sau -
-
Xác định bản đồ m và maxDepth
-
Xác định một phương thức đệ quy giải quyết (), điều này sẽ lấy nút và cấp, cấp ban đầu là 0
-
nếu nút không có, thì trả về
-
maxDepth:=max của cấp và maxDepth
-
tăng m [cấp] theo giá trị của nút
-
giải quyết (bên trái của nút, mức + 1)
-
giải quyết (bên phải của nút, mức + 1)
-
Trong phương thức chính, thiết lập maxDepth:=0, sau đó giải quyết (root, 0)
-
trả về m [maxDepth]
Hãy cùng chúng tôi xem cách triển khai sau để hiểu rõ hơn -
Ví dụ
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth;
map <int, int> m;
void solve(TreeNode* node, int level = 0){
if(!node)return;
maxDepth = max(level, maxDepth);
m[level] += node->val;
solve(node->left, level + 1);
solve(node->right, level + 1);
}
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
maxDepth = 0;
m.clear();
solve(root);
return m[maxDepth];
}
};
main(){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(1);
root−>left = new TreeNode(2);
root−>right = new TreeNode(3);
root−>left−>left = new TreeNode(4);
root−>left−>right = new TreeNode(5);
root−>right−>right = new TreeNode(6);
root−>right−>right−>right = new TreeNode(4);
root−>left−>left−>left = new TreeNode(7);
Solution ob;
cout << (ob.deepestLeavesSum(root));
} Đầu vào
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(1); root−>left = new TreeNode(2); root−>right = new TreeNode(3); root−>left−>left = new TreeNode(4); root−>left−>right = new TreeNode(5); root−>right−>right = new TreeNode(6); root−>right−>right−>right = new TreeNode(4); root−>left−>left−>left = new TreeNode(7);
Đầu ra
11
