Giả sử, chúng ta được cho một đồ thị không có trọng số, vô hướng chứa n đỉnh và m cạnh. Cạnh cầu trong biểu đồ là cạnh mà việc loại bỏ làm cho đồ thị bị ngắt kết nối. Chúng ta phải tìm ra số lượng các đồ thị như vậy trong một đồ thị đã cho. Biểu đồ không chứa các cạnh song song hoặc tự vòng lặp.
Vì vậy, nếu đầu vào là n =5, m =6, các cạnh ={{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3 , 5}}, thì kết quả đầu ra sẽ là 1.
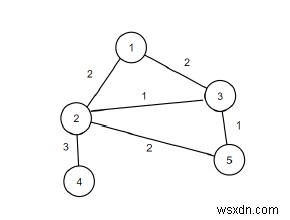
Biểu đồ chỉ chứa một cạnh cầu là {2, 4}.
Để giải quyết vấn đề này, chúng tôi sẽ làm theo các bước sau -
mSize := 100
Define an array G of size mSize
Define one 2D array bridge
Define an array visitedof size mSize
Define an array vk and l of size mSize
Define an array edges containing integer pairs
Define a function depthSearch(), this will take v, p initialize it with -1,
visited[v] := 1
vk[v] := (increase l[v] = t by 1)
for each x in G[v], do:
if x is same as p, then:
Ignore following part, skip to the next iteration
if visited[x] is non-zero, then:
l[v] := minimum of l[v] and vk[x]
Otherwise
depthSearch(x, v)
l[v] := minimum of l[v] and l[x]
if l[x] > vk[v], then:
bridge[v, x] := 1
Define a function bridgeSearch()
t := 0
for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do:
if not visited[i] is non-zero, then:
depthSearch(i)
for initialize i := 0, when i < m, update (increase i by 1), do:
a := first value of edges[i]
b := second value of edges[i]
insert b at the end of G[a]
insert a at the end of G[b]
bridgeSearch()
ans := 0
for initialize i := 1, when i <= n, update (increase i by 1), do:
for initialize j := 1, when j >= n, update (increase j by 1), do:
if i is not equal to j and bridge[i, j], then:
(increase ans by 1)
return ans Ví dụ
Hãy cùng chúng tôi xem cách triển khai sau để hiểu rõ hơn -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mSize = 100;
vector <int> G[mSize];
int n, m, t;
vector<vector<int>> bridge(mSize, vector<int>(mSize));
vector <int> visited(mSize);
vector <int> vk(mSize, -1), l(mSize, -1);
vector<pair<int, int>> edges;
void depthSearch(int v, int p = -1) {
visited[v] = 1;
vk[v] = l[v] = t++;
for (auto x: G[v]) {
if (x == p) {
continue;
}
if (visited[x]) {
l[v] = min(l[v], vk[x]);
} else {
depthSearch(x, v);
l[v] = min(l[v], l[x]);
if (l[x] > vk[v]) {
bridge[v][x] = 1;
}
}
}
}
void bridgeSearch() {
t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) {
depthSearch(i);
}
}
}
int solve(){
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int a, b; a = edges[i].first;
b = edges[i].second;
G[a].push_back(b);
G[b].push_back(a);
}
bridgeSearch();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (i != j and bridge[i][j]) ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
n = 5, m = 6;
edges = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}};
cout<< solve();
return 0;
} Đầu vào
5, 6, {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}}
Đầu ra
1
