Trong hướng dẫn này, chúng tôi sẽ tạo một máy tính GUI đơn giản bằng cách sử dụng Tkinter mô-đun. Tkinter là nội dung mô-đun Python để phát triển ứng dụng GUI. Nó dễ sử dụng và đi kèm với Python. Chúng tôi có thể trực quan hóa dữ liệu của mình bằng các ứng dụng GUI.
Hãy xem cách tạo một máy tính GUI đơn giản.
-
Nhập mọi thứ từ Tkinter bằng cách sử dụng *.
-
Tạo giao diện cho máy tính.
-
Tạo một hàm nhập để nhập một số vào trường nhập.
-
Tạo một hàm rõ ràng xóa sạch mọi thứ khỏi trường đầu vào.
-
Và cuối cùng, đánh giá hàm tính toán và đưa ra kết quả của biểu thức.
Ví dụ
# importing everyting from tkinter
from tkinter import *
# expression to access among all the functions
expression = ""
# functions
def input_number(number, equation):
# accessing the global expression variable
global expression
# concatenation of string
expression = expression + str(number)
equation.set(expression)
def clear_input_field(equation):
global expression
expression = ""
# setting empty string in the input field
equation.set("Enter the expression")
def evaluate(equation):
global expression
# trying to evaluate the expression
try:
result = str(eval(expression))
# showing the result in the input field
equation.set(result)
# setting expression to empty string
expression = ""
except:
# some error occured
# showing it to the user equation.set("Enter a valid expression")
expression = ""
# creating the GUI
def main():
# main window window = Tk()
# setting the title of GUI window
window.title("Calculator")
# set the configuration of GUI window
window.geometry("325x175")
# varible class instantiation
equation = StringVar()
# input field for the expression
input_field = Entry(window, textvariable=equation)
input_field.place(height=100)
# we are using grid position
# for the arrangement of the widgets
input_field.grid(columnspan=4, ipadx=100, ipady=5)
# settin the placeholder message for users
equation.set("Enter the expression")
# creating buttons and placing them at respective positions
_1 = Button(window, text='1', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(1, equation), height=2, width=7)
_1.grid(row=2, column=0)
_2 = Button(window, text='2', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(2, equation), height=2, width=7)
_2.grid(row=2, column=1)
_3 = Button(window, text='3', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(3, equation), height=2, width=7)
_3.grid(row=2, column=2)
_4 = Button(window, text='4', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(4, equation), height=2, width=7)
_4.grid(row=3, column=0)
_5 = Button(window, text='5', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(5, equation), height=2, width=7)
_5.grid(row=3, column=1)
_6 = Button(window, text='6', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(6, equation), height=2, width=7)
_6.grid(row=3, column=2)
_7 = Button(window, text='7', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(7, equation), height=2, width=7)
_7.grid(row=4, column=0)
_8 = Button(window, text='8', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(8, equation), height=2, width=7)
_8.grid(row=4, column=1)
_9 = Button(window, text='9', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(9, equation), height=2, width=7)
_9.grid(row=4, column=2)
_0 = Button(window, text='0', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number(0, equation), height=2, width=7)
_0.grid(row=5, column=0)
plus = Button(window, text='+', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number('+', equation), height=2, width=7)
plus.grid(row=2, column=3)
minus = Button(window, text='-', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number('-', equation), height=2, width=7)
minus.grid(row=3, column=3)
multiply = Button(window, text='*', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number('*', equation), height=2, width=7)
multiply.grid(row=4, column=3)
divide = Button(window, text='/', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: input_number('/', equation), height=2, width=7)
divide.grid(row=5, column=3)
equal = Button(window, text='=', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: evaluate(equation), height=2, width=7)
equal.grid(row=5, column=2)
clear = Button(window, text='Clear', fg='white', bg='black', bd=0, command=lambda: clear_input_field(equation), height=2, width=7)
clear.grid(row=5, column=1)
# showing the GUI
window.mainloop()
# start of the program
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Đầu ra
Nếu bạn chạy chương trình trên, bạn sẽ nhận được một máy tính đơn giản như sau.
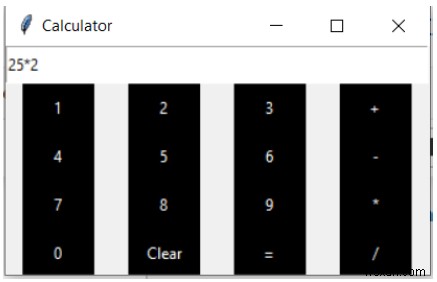
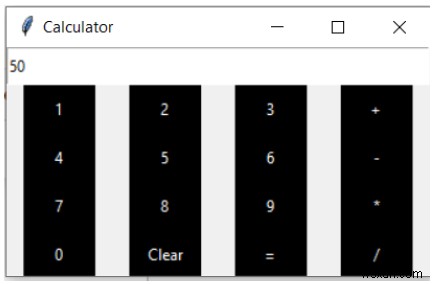
Kết quả của biểu thức trên được tạo sau nút pression =.
Kết luận
Nếu bạn có bất kỳ nghi ngờ nào trong hướng dẫn, hãy đề cập đến chúng trong phần bình luận.
