Nếu bạn đã từng thắc mắc về cách các hộp thoại hoạt động trong một ứng dụng Python, thì có thể bạn sẽ nghe thấy danh sách hồ sơ mô-đun trong Tkinter. Hồ sơ lưu trữ mô-đun chứa một số chức năng tích hợp có thể được sử dụng để hiển thị các loại hộp thoại khác nhau để xử lý các tệp trong hệ thống.
Trong hầu hết các trường hợp, chúng tôi sử dụng tệp tin tên miền () chức năng yêu cầu người dùng duyệt và mở một tập tin từ hệ thống. Dựa trên việc lựa chọn loại tệp, tập lệnh được lập trình để thực hiện thao tác ghi hoặc đọc.
Sau khi tệp được mở, bạn có thể sử dụng mở (tệp, 'chế độ') có chức năng mở và thực hiện các thao tác ở bất kỳ chế độ nào. Để chứng minh điều này, hãy lấy một ví dụ trong đó chúng ta sẽ tạo một ứng dụng yêu cầu người dùng mở một tệp văn bản. Sau khi tệp được chọn và mở, chúng tôi có thể đọc tệp này bằng chế độ hoạt động "đọc".
Ví dụ
# Import the library
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import filedialog
# Create an instance of window
win=Tk()
# Set the geometry of the window
win.geometry("700x300")
# Create a label
Label(win, text="Click the button to open a dialog", font='Arial 16 bold').pack(pady=15)
# Function to open a file in the system
def open_file():
filepath = filedialog.askopenfilename(title="Open a Text File", filetypes=(("text files","*.txt"), ("all files","*.*")))
file = open(filepath,'r')
print(file.read())
file.close()
# Create a button to trigger the dialog
button = Button(win, text="Open", command=open_file)
button.pack()
win.mainloop() Đầu ra
Chạy đoạn mã trên sẽ hiển thị một cửa sổ có nút để mở hộp thoại.
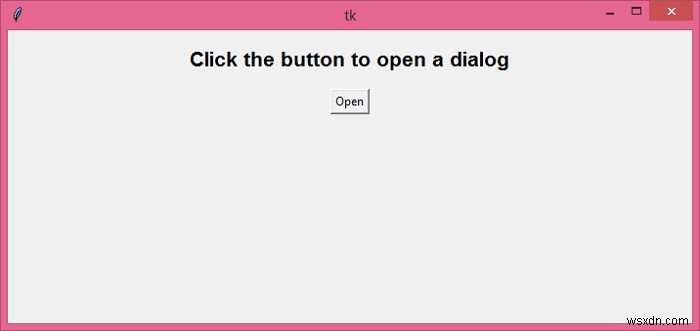
Chọn và mở một tệp văn bản và bảng điều khiển sẽ hiển thị tất cả nội dung của tệp.
Centralized Database Vs Blockchain A blockchain can be both permissionless (like Bitcoin or Ethereum) or permissioned (like the different Hyperledger blockchain frameworks). A permissionless blockchain is also known as a public blockchain, because anyone can join the network. A permissioned blockchain, or private blockchain, requires pre-verification of the participating parties within the network, and these parties are usually known to each other. Types of Blockchains The choice between permissionless versus permissioned blockchains should be driven by the particular application at hand (or use case). Most enterprise use cases involve extensive vetting before parties agree to do business with each other. An example where a number of businesses exchange information is supply chain management. The supply chain management is an ideal use case for permissioned blockchains. You would only want trusted parties participating in the network. Each participant that is involved in the supply chain would require permissions to execute transactions on the blockchain. These transactions would allow other companies to understand where in the supply chain a particular item is.
