Chúng ta phải in dữ liệu của các nút của danh sách liên kết tại chỉ mục đã cho. Không giống như danh sách liên kết mảng thường không có chỉ mục, vì vậy chúng tôi phải duyệt qua toàn bộ danh sách được liên kết và in dữ liệu khi chúng tôi đến một danh sách cụ thể.
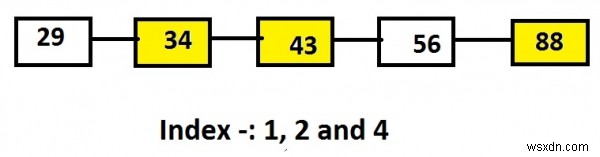
Giả sử, danh sách chứa các nút 29, 34, 43, 56 và 88 và giá trị của các chỉ mục là 1, 2 và 4 so với đầu ra sẽ là các nút tại các chỉ mục này là 34, 43 và 88.
Ví dụ
Linked list: 29->34->43->56->88 Input: 1 2 4 Output: 34 43 88
Trong biểu diễn trên của Danh sách được liên kết, các nút được đánh dấu màu vàng là các nút được in hoặc các nút nằm trên một chỉ mục cụ thể.
Cách tiếp cận được sử dụng ở đây liên quan đến việc lấy một con trỏ và một biến đếm được khởi tạo thành 1 sẽ tăng lên bất cứ khi nào nút được duyệt. Bộ đếm được khớp với giá trị khóa. Khi khóa khớp với giá trị bộ đếm, con trỏ trỏ đến cấu trúc nút sẽ in dữ liệu của nút và tăng dần đến nút tiếp theo, v.v. cung cấp cho chúng ta các nút tại khóa cụ thể.
Đoạn mã dưới đây cho thấy cách triển khai c của thuật toán đã cho.
Thuật toán
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *next Step 2 -> create struct node* intoList(int data) Create newnode using malloc Set newnode->data = data newnode->next = NULL return newnode step 3 -> Declare function void displayList(struct node *catchead) create struct node *temp IF catchead = NULL Print list is empty return End Set temp = catchead Loop While (temp != NULL) print temp->data set temp = temp->next End Step 4 -> Declare Function int search(int key,struct node *head) Set int index Create struct node *newnode Set index = 0 and newnode = head Loop While (newnode != NULL & newnode->data != key) Set index++ Set newnode = newnode->next End return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1 step 5 -> In Main() create node using struct node* head = intoList(9) call displayList(head) set index = search(24,head) IF (index >= 0) Print index Else Print not found in the list EndIF STOP
Ví dụ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* intoList(int data) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//funtion to display list
void displayList(struct node *catchead) {
struct node *temp;
if (catchead == NULL) {
printf("List is empty.\n");
return;
}
printf("elements of list are : ");
temp = catchead;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//function to search element
int search(int key,struct node *head) {
int index;
struct node *newnode;
index = 0;
newnode = head;
while (newnode != NULL && newnode->data != key) {
index++;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1;
}
int main() {
int index;
struct node* head = intoList(9); //inserting elements into a list
head->next = intoList(76);
head->next->next = intoList(13);
head->next->next->next = intoList(24);
head->next->next->next->next = intoList(55);
head->next->next->next->next->next = intoList(109);
displayList(head);
index = search(24,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 24, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 24);
index=search(55,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 55, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 55);
} Đầu ra
Nếu chúng ta chạy chương trình trên thì nó sẽ tạo ra kết quả sau.
elements of list are : 9 76 13 24 55 109 24 found at position 3 55 found at position 4
