Cho một chuỗi bao gồm các giá trị số, nhiệm vụ là giấu những số đã cho đó thành lời.
Giống như chúng ta có đầu vào “361”; thì đầu ra phải ở dạng từ, tức là "Ba trăm sáu mươi mốt". Đối với giải pháp của vấn đề sau, chúng ta phải ghi nhớ các con số và vị trí của nó như hàng đơn vị, hàng chục, hàng nghìn, v.v.
Mã chỉ hỗ trợ tối đa 4 chữ số, tức là, 0 đến 9999. Vì vậy, đầu vào phải từ 0 đến 9999.
Chúng ta hãy xem xét 1.111 địa điểm sẽ như thế nào -
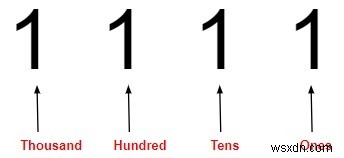
Ví dụ
Input: “1234” Output: one thousand two hundred thirty four Input: “7777” Output: seven thousand seven hundred seventy seven
Phương pháp tiếp cận mà chúng tôi sẽ sử dụng để giải quyết vấn đề đã cho -
- Lấy đầu vào dưới dạng một chuỗi.
- Tạo mảng cho các giá trị khác nhau.
- Kiểm tra độ dài của đầu vào theo độ dài, chúng tôi sẽ quyết định xem chúng tôi sẽ hiển thị đầu ra ở vị trí nào.
- Tùy theo địa điểm sẽ hiển thị kết quả đầu ra.
Thuật toán
Start
Step 1 → In function convert(char *num)
Declare and initialize int len = strlen(num)
If len == 0 then,
fprintf(stderr, "empty string\n")
Return
End If
If len > 4 then,
fprintf(stderr, "Length more than 4 is not supported\n")
Return
End If
Declare and initialize a char *single_digit[] = { "zero", "one", "two","three", "four","five","six", "seven", "eight", "nine"}
Declare and initialize a char *tens_place[] = {"", "ten", "eleven", "twelve","thirteen", "fourteen","fifteen", "sixteen","seventeen", "eighteen", "nineteen"}
Declare and Initialize a char *tens_multiple[] = {"", "", "twenty", "thirty", "forty", "fifty","sixty", "seventy", "eighty", "ninety"}
Declare and initialize char *tens_power[] = {"hundred", "thousand"}
Print num
If len == 1 then,
Print single_digit[*num - '0']
Return
End If
While *num != '\0
If len >= 3
If *num -'0' != 0
Print single_digit[*num - '0']
Print tens_power[len-3]
End If
Decrement len by 1
End If
Else
If *num == '1' then,
Set sum = *num - '0' + *(num + 1)- '0'
Print tens_place[sum]
Return
End If
Else If *num == '2' && *(num + 1) == '0' then,
Print “twenty”
Return
End else If
Else
Set i = *num - '0'
Print i? tens_multiple[i]: ""
Increment num by 1
If *num != '0' then,
Print single_digit[*num - '0']
End If
End Else
Increment num by 1
End Else
End while
Step 2 → In function main()
Call function convert("9132")
Stop Ví dụ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//function to print the given number in words
void convert(char *num) {
int len = strlen(num);
// cases
if (len == 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "empty string\n");
return;
}
if (len > 4) {
fprintf(stderr, "Length more than 4 is not supported\n");
return;
}
// the first string wont be used.
char *single_digit[] = { "zero", "one", "two", "three", "four","five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine"};
// The first string is not used, it is to make
// array indexing simple
char *tens_place[] = {"", "ten", "eleven", "twelve", "thirteen", "fourteen", "fifteen", "sixteen", "seventeen", "eighteen", "nineteen"};
// The first two string are not used, they are to make
// array indexing simple
char *tens_multiple[] = {"", "", "twenty", "thirty", "forty", "fifty","sixty", "seventy", "eighty", "ninety"};
char *tens_power[] = {"hundred", "thousand"};
// Used for debugging purpose only
printf("\n%s: ", num);
// For single digit number
if (len == 1) {
printf("%s\n", single_digit[*num - '0']);
return;
}
// Iterate while num is not '\0'
while (*num != '\0') {
// Code path for first 2 digits
if (len >= 3) {
if (*num -'0' != 0) {
printf("%s ", single_digit[*num - '0']);
printf("%s ", tens_power[len-3]); // here len can be 3 or 4
}
--len;
}
// Code path for last 2 digits
else {
// Need to explicitly handle 10-19. Sum of the two digits is
//used as index of "tens_place" array of strings
if (*num == '1') {
int sum = *num - '0' + *(num + 1)- '0';
printf("%s\n", tens_place[sum]);
return;
}
// Need to explicitely handle 20
else if (*num == '2' && *(num + 1) == '0') {
printf("twenty\n");
return;
}
// Rest of the two digit numbers i.e., 21 to 99
else {
int i = *num - '0';
printf("%s ", i? tens_multiple[i]: "");
++num;
if (*num != '0')
printf("%s ", single_digit[*num - '0']);
}
}
++num;
}
}
int main() {
convert("9132");
return 0;
} Đầu ra
nine thousand one hundred thirty two
